Rituximab-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- PMID: 18843175
- PMCID: PMC2790794
- DOI: 10.1159/000163069
Rituximab-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Abstract
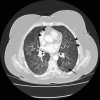
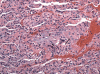
Rituximab is a chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody used to treat CD20+ non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Although pulmonary adverse reactions such as cough, rhinitis, bronchospasm, dyspnea and sinusitis are relatively common, other respiratory conditions like cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, interstitial pneumonitis and diffuse alveolar hemorrhage have rarely been reported. Only 2 possible cases of rituximab-associated hypersensitivity pneumonitis have been described to date. We present a case of hypersensitivity pneumonitis with classic radiographic and histopathologic findings in a patient treated with rituximab who responded to prednisone.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rituximab-induced subacute interstitial pneumonitis: a case report and review of literature.J Cancer Res Ther. 2010 Jul-Sep;6(3):344-6. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.73356. J Cancer Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 21119272 Review.
-
Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia after rituximab therapy for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Hematol Oncol. 2006 Dec;24(4):234-7. doi: 10.1002/hon.799. Hematol Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16948177
-
Fatal cytokine release syndrome with chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in a 71-year-old patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.J Clin Oncol. 1999 Jun;17(6):1962-3. doi: 10.1200/jco.1999.17.6.1962. J Clin Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10561242 No abstract available.
-
A fatal case of alemtuzumab-associated interstitial pneumonitis.Am J Ther. 2008 Jan-Feb;15(1):82-4. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181400395. Am J Ther. 2008. PMID: 18223357
-
[Current status and measures for lung injuries in cancer treatment].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2004 May;31(5):679-84. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2004. PMID: 15170972 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Organizing Pneumonia and Immunomediated Colitis Associated with Ocrelizumab Treatment.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2025 Mar 1;28(2):276-278. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_608_24. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39878418 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A case series of patients on chemotherapy with dyspnoea and pulmonary infiltrates.BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Jun 5;2013:bcr2013009105. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-009105. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23744855 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Steroid-Responsive Severe Pneumonia Following a Recent COVID-19 Infection in a Patient With Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated With Streptococcal Infection.Cureus. 2022 Jul 12;14(7):e26785. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26785. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35967156 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical review: Serious adverse events associated with the use of rituximab - a critical care perspective.Crit Care. 2012 Aug 31;16(4):231. doi: 10.1186/cc11304. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22967460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rituximab-induced bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia.Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:680431. doi: 10.1155/2012/680431. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Case Rep Med. 2012. PMID: 22778751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bienvenu J, Chvetzoff R, Salles G, Balter C, Tilly H, Herbrecht R, Morel P, Lederlin P, Solal-Celigny P, Audhuy B, Christian B, Gabarre J, Casasnovas O, Marit G, Sebban C, Coiffier B, Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte Tumor necrosis factor alpha release is a major biological event associated with rituximab treatment. Hematol J. 2001;2:378–384. - PubMed
-
- Winkler U, Jensen M, Manzke O, Schulz H, Diehl V, Engert A. Cytokine-release syndrome in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and high lymphocyte counts after treatment with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab, IDEC-C2B8) Blood. 1999;94:2217–2224. - PubMed
-
- van der Kolk LE, Grillo-López AJ, Baars JW, Hack CE, van Oers MH. Complement activation plays a key role in the side-effects of rituximab treatment. Br J Haematol. 2001;115:807–811. - PubMed
-
- Genentech: Rituxan: highlights of prescribing information, revised January 2008. http://www.gene.com/gene/products/information/pdf/rituxan-prescribing.pdf
-
- Bellosillo B, Villamor N, López-Guillermo A, Marcé S, Esteve J, Campo E, Colomer D, Montserrat E. Complement-mediated cell death induced by rituximab in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders is mediated in vitro by a caspase-independent mechanism involving the generation of reactive oxygen species. Blood. 2001;98:2771–2777. - PubMed
