Elucidating rifampin's inducing and inhibiting effects on glyburide pharmacokinetics and blood glucose in healthy volunteers: unmasking the differential effects of enzyme induction and transporter inhibition for a drug and its primary metabolite
- PMID: 18843263
- PMCID: PMC3582657
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2008.186
Elucidating rifampin's inducing and inhibiting effects on glyburide pharmacokinetics and blood glucose in healthy volunteers: unmasking the differential effects of enzyme induction and transporter inhibition for a drug and its primary metabolite
Abstract
The effects of single doses of intravenous (IV) ciprofloxacin and rifampin and of multiple doses of rifampin on glyburide exposure and blood glucose levels were investigated in nine healthy volunteers. A single IV dose of rifampin significantly increased the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of glyburide and its metabolite. Blood glucose levels were significantly lower than those observed after dosing with glyburide alone. Multiple doses of rifampin induced an increase in liver enzyme levels, leading to a marked decrease in glyburide exposure and blood glucose levels. When IV rifampin was administered after multiple doses of rifampin, the inhibition of hepatic uptake transporters masked the induction effect; however, the relative changes in AUC for glyburide and its hydroxyl metabolite were similar to those seen under noninduced conditions. The studies reported here demonstrate how measurements of the levels of both the parent drug and its primary metabolite are useful in unmasking simultaneous drug-drug induction and inhibition effects and in characterizing enzymatic vs. transporter mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
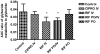

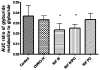

References
-
- Abe T, et al. Identification of a novel gene family encoding human liver-specific organic anion transporter LST-1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17159–17163. - PubMed
-
- Konig J, Cui Y, Nies AT, Keppler D. A novel human organic anion transporting polypeptide localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Am J Physiol - Gastrointestinal & Liver Physiology. 2000;278:G156–G164. - PubMed
-
- Konig J, Cui Y, Nies AT, Keppler D. Localization and genomic organization of a new hepatocellular organic anion transporting polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:23161–23168. - PubMed
-
- Satoh H, et al. Citrus juices inhibit the function of human organic anion-transporting polypeptide OATP-B. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005;33:518–523. - PubMed
-
- Wu CY, Benet LZ. Predicting drug disposition via application of BCS: transport/absorption/elimination interplay and development of a biopharmaceutics drug disposition classification system. Pharm Res. 2005;22:11–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

