Effects of topiramate and other anti-glutamatergic drugs on the acute intoxicating actions of ethanol in mice: modulation by genetic strain and stress
- PMID: 18843265
- PMCID: PMC2669690
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2008.182
Effects of topiramate and other anti-glutamatergic drugs on the acute intoxicating actions of ethanol in mice: modulation by genetic strain and stress
Abstract
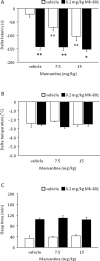
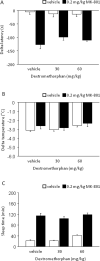
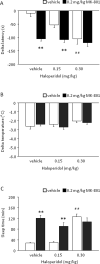
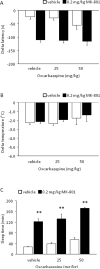
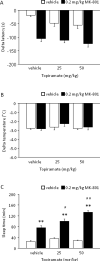
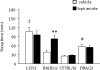
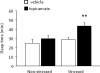
Compounds with anti-glutamatergic properties currently in clinical use for various indications (eg Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, psychosis, mood disorders) have potential utility as novel treatments for alcoholism. Enhanced sensitivity to certain acute intoxicating effects (ataxia, sedative) of alcohol may be one mechanism by which anti-glutamatergic drugs modulate alcohol use. We examined the effects of six compounds (memantine, dextromethorphan, haloperidol, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, and topiramate) on sensitivity to acute intoxicating effects of ethanol (ataxia, hypothermia, sedation/hypnosis) in C57BL/6J mice. Analysis of topiramate was extended to determine the influence of genetic background (by comparison of the 129S1, BALB/cJ, C57BL/6J, DBA/2J inbred strains) and prior stress history (by chronic exposure of C57BL/6J to swim stress) on topiramate's effects on ethanol-induced sedation/hypnosis. Results showed that one N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist, memantine, but not another, dextromethorphan, potentiated the ataxic but not hypothermic or sedative/hypnotic effects of ethanol. Haloperidol increased ethanol-induced ataxia and sedation/hypnosis to a similar extent as the prototypical NMDAR antagonist MK-801. Of the anticonvulsants tested, lamotrigine accentuated ethanol-induced sedation/hypnosis, whereas oxcarbazepine was without effect. Topiramate was without effect per se under baseline conditions in C57BL/6J, but had a synergistic effect with MK-801 on ethanol-induced sedation/hypnosis. Comparing inbred strains, topiramate was found to significantly potentiate ethanol's sedative/hypnotic effects in BALB/cJ, but not 129S1, C57BL/6J, or DBA/2J strains. Topiramate also increased ethanol-induced sedation/hypnosis in C57BL/6J after exposure to chronic stress exposure. Current data demonstrate that with the exception of MK-801 and haloperidol, the compounds tested had either no significant or assay-selective effects on sensitivity to acute ethanol under baseline conditions in C57BL/6J. However, significant effects of topiramate were revealed as a function of co-treatment with an NMDAR blocker, genetic background, or prior stress history. These findings raise the possibility that topiramate and possibly other anti-glutamatergic drugs could promote the acute intoxicating effects of ethanol in specific subpopulations defined by genetics or life history.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of major NMDA or AMPA receptor subunits in MK-801 potentiation of ethanol intoxication.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008 Aug;32(8):1479-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00715.x. Epub 2008 Jun 28. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008. PMID: 18565157 Free PMC article.
-
Topiramate does not affect the acquisition or expression of ethanol conditioned place preference in DBA/2J or C57BL/6J mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006 May;30(5):783-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00091.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006. PMID: 16634846
-
Chronic swim stress alters sensitivity to acute behavioral effects of ethanol in mice.Physiol Behav. 2007 May 16;91(1):77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.01.024. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Physiol Behav. 2007. PMID: 17363014
-
Oxcarbazepine, topiramate, zonisamide, and levetiracetam: potential use in neuropathic pain.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2003 Sep;1(1):18-37. doi: 10.1016/s1543-5946(03)80013-2. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2003. PMID: 15555463 Review.
-
Comparative anticonvulsant and mechanistic profile of the established and newer antiepileptic drugs.Epilepsia. 1999;40 Suppl 5:S2-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1999.tb00913.x. Epilepsia. 1999. PMID: 10530688 Review.
Cited by
-
Amantadine and cognitive flexibility: decision making in Parkinson's patients with severe pathological gambling and other impulse control disorders.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Jun 17;10:1093-101. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S54423. eCollection 2014. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014. PMID: 24971012 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of GluK1-containing kainate receptors reduces ethanol consumption by modulating ethanol reward and withdrawal.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Nov 1;199:108783. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108783. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34509497 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait loci for sensitivity to ethanol intoxication in a C57BL/6J×129S1/SvImJ inbred mouse cross.Mamm Genome. 2012 Jun;23(5-6):305-21. doi: 10.1007/s00335-012-9394-2. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Mamm Genome. 2012. PMID: 22371272 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerance to ethanol intoxication after chronic ethanol: role of GluN2A and PSD-95.Addict Biol. 2015 Mar;20(2):259-62. doi: 10.1111/adb.12110. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Addict Biol. 2015. PMID: 24397780 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse strain differences in punished ethanol self-administration.Alcohol. 2017 Feb;58:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Alcohol. 2017. PMID: 27814928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad S, Fowler LJ, Whitton PS. Effects of acute and chronic lamotrigine treatment on basal and stimulated extracellular amino acids in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. Brain Res. 2004b;1029:41–7. - PubMed
-
- Aracava Y, Pereira EF, Maelicke A, Albuquerque EX. Memantine blocks alpha7* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors more potently than n-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;312:1195–205. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom P, Bachteler D, Koch S, Hyytia P, Spanagel R. mGluR5 antagonist MPEP reduces ethanol-seeking and relapse behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:921–8. - PubMed
-
- Becker HC, Lopez MF. Increased ethanol drinking after repeated chronic ethanol exposure and withdrawal experience in C57BL/6 mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004;28:1829–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

