Bone marrow microenvironment and the identification of new targets for myeloma therapy
- PMID: 18843284
- PMCID: PMC3418600
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2008.259
Bone marrow microenvironment and the identification of new targets for myeloma therapy
Abstract
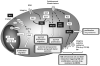
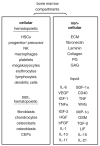
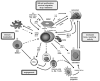
The development of multiple myeloma (MM) is a complex multi-step process involving both early and late genetic changes in the tumor cell as well as selective supportive conditions by the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment. Indeed, it is now well established that MM cell-induced disruption of the BM homeostasis between the highly organized cellular and extracellular compartments supports MM cell proliferation, survival, migration and drug resistance through activation of various signaling (for example, PI3K/Akt, JAK/Stat-, Raf/MEK/MAPK-, NFkappaB- and Wnt-) pathways. Based on our enhanced understanding of the functional importance of the MM BM microenvironment and its inter-relation with the MM cell resulting in homing, seeding, proliferation and survival, new molecular targets have been identified and derived treatment regimens in MM have already changed fundamentally during recent years. These agents include thalidomide, its immunomodulatory derivative lenalidomide and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, which mediate tumor cytotoxicity in the BM milieu. Ongoing studies are further delineating MM pathogenesis in the BM to enhance cytotoxicity, avoid drug resistance and improve patient outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Fonseca R, Bailey RJ, Ahmann GJ, Rajkumar SV, Hoyer JD, Lust JA, et al. Genomic abnormalities in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Blood. 2002;100:1417–1424. - PubMed
-
- Zhan F, Hardin J, Kordsmeier B, Bumm K, Zheng M, Tian E, et al. Global gene expression profiling of multiple myeloma, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, and normal bone marrow plasma cells. Blood. 2002;99:1745–1757. - PubMed
-
- Keats JJ, Reiman T, Belch AR, Pilarski LM. Ten years and counting: so what do we know about t(4;14)(p16;q32) multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006;47:2289–2300. - PubMed
-
- Carrasco DR, Tonon G, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Sinha R, Feng B, et al. High-resolution genomic profiles define distinct clinico-pathogenetic subgroups of multiple myeloma patients. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:313–325. - PubMed
-
- Hazlehurst LA, Landowski TH, Dalton WS. Role of the tumor microenvironment in mediating de novo resistance to drugs and physiological mediators of cell death. Oncogene. 2003;22:7396–7402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous