Nerve transfer for elbow flexion in radiation-induced brachial plexopathy: a case report
- PMID: 18843522
- PMCID: PMC2686782
- DOI: 10.1007/s11552-008-9136-9
Nerve transfer for elbow flexion in radiation-induced brachial plexopathy: a case report
Abstract
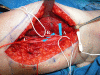
Radiation-induced brachial plexopathy is an uncommon but devastating late complication seen in patients receiving radiation therapy to the chest wall and axilla. Treatment options are unfortunately limited. We report a case of a 59-year-old woman treated with radiation therapy for breast cancer 12 years earlier, who presented with loss of elbow flexion and marked shoulder weakness. Electromyogram and intraoperative stimulation of the musculocutaneous nerve branches were consistent with a proximal motor nerve conduction block. Microsurgical transfer of median and ulnar nerve fascicles to the biceps and brachialis branches of the musculocutaneous nerve, respectively, were performed. The patient recovered MRC grade 4/5 elbow flexion after surgery. The characteristics of this disorder and surgical treatment options are reviewed.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources