Selective estrogen receptor modulators and phytoestrogens
- PMID: 18843590
- PMCID: PMC2587438
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0028-1088304
Selective estrogen receptor modulators and phytoestrogens
Abstract
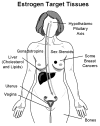
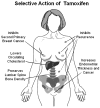
Scientific achievements in the last two decades have revolutionized the treatment and prevention of breast cancer. This is mainly because of targeted therapies and a better understanding of the relationship between estrogen, its receptor, and breast cancer. One of these discoveries is the use of synthetic selective estrogen modulators (SERMs) such as tamoxifen in the treatment strategy for estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer. Hundreds of thousands of lives have been saved because of this advance. Not only is tamoxifen used in the treatment strategy for patients who have breast cancer, but also for prevention in high-risk premenopausal women. Another synthetic SERM, raloxifene, which was initially used to prevent osteoporosis, is also as effective as tamoxifen for prevention in high-risk postmenopausal women. In certain regions of the world, particularly in Asia, a low incidence of breast cancer has been observed. These women have diets that are high in soy and low in fat, unlike the Western diet. Interest in the protective effects of soy derivatives has led to the research of phytoestrogens and metabolites of soy that are described by some as natural SERMs. As a result, many clinical questions have been raised as to whether phytoestrogens, which are also found in other natural foods, can protect against breast cancer. This article reviews the development and role of the more common SERMs, tamoxifen and raloxifene. In addition, this paper will also highlight the emerging studies on phytoestrogens and their similarity and dissimilarity to SERMs.
Figures
References
-
- Jordan VC. Tamoxifen: a most unlikely pioneering medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:205–13. - PubMed
-
- Boyd S. On oophorectomy in cancer of the breast. B M J. 1900;ii:1161–7.
-
- Allen E, Doisy EA. An ovarian hormone: Preliminary reports on its localization, extraction and partial purification and action in test animals. JAMA. 1923;81:810–21. - PubMed
-
- Lacassagne A. Hormonal pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma of the breast. Am J Cancer. 1936;27:217–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials