Blood pressure lowering efficacy of angiotensin receptor blockers for primary hypertension
- PMID: 18843650
- PMCID: PMC6669255
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003822.pub2
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of angiotensin receptor blockers for primary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are widely prescribed for hypertension so it is essential to determine and compare their effects on blood pressure (BP), heart rate and withdrawals due to adverse effects (WDAE).
Objectives: To quantify the dose-related systolic and/or diastolic BP lowering efficacy of ARBs versus placebo in the treatment of primary hypertension.
Search strategy: We searched CENTRAL (The Cochrane Library 2007, Issue 1), MEDLINE (1966 to February 2007), EMBASE (1988 to February 2007) and reference lists of articles.
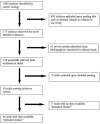
Selection criteria: Double-blind, randomized, controlled trials evaluating the BP lowering efficacy of fixed-dose monotherapy with an ARB compared with placebo for a duration of 3 to 12 weeks in patients with primary hypertension.
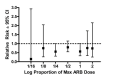
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information. WDAE information was collected from the trials.
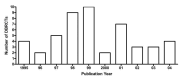
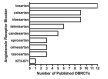
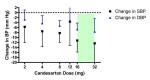
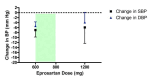
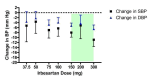
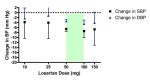
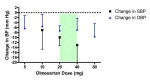
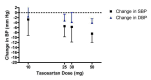
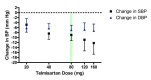
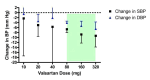
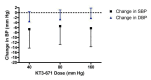
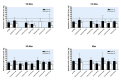
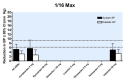
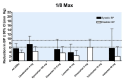
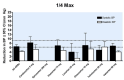
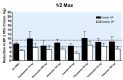
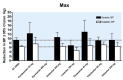
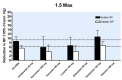
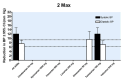
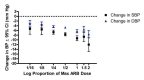
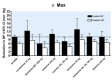
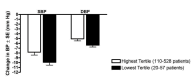
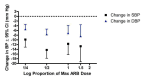
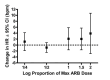
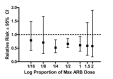
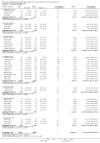
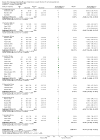
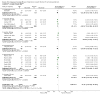
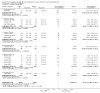
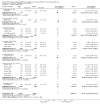
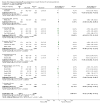
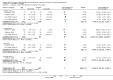
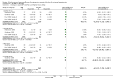
Main results: Forty six RCTs evaluated the dose-related trough BP lowering efficacy of 9 ARBs in 13 451 participants with a baseline BP of 156/101 mm Hg. The data do not suggest that any one ARB is better or worse at lowering BP. A dose of 1/8 or 1/4 of the manufacturers' maximum recommended daily dose (Max) achieved a BP lowering effect that was 60 to 70% of the BP lowering effect of Max. A dose of 1/2 Max achieved a BP lowering effect that was 80% of Max. ARB doses above Max did not significantly lower BP more than Max. Due to evidence of publication bias, the largest trials provide the best estimate of the trough BP lowering efficacy for ARBs as a class of drugs: -8 mm Hg for SBP and -5 mm Hg for DBP. ARBs reduced BP measured 1 to 12 hours after the dose by about 12/7 mm Hg.
Authors' conclusions: The evidence from this review suggests that there are no clinically meaningful BP lowering differences between available ARBs. The BP lowering effect of ARBs is modest and similar to ACE inhibitors as a class; the magnitude of average trough BP lowering for ARBs at maximum recommended doses and above is -8/-5 mmHg. Furthermore, 60 to 70% of this trough BP lowering effect occurs with recommended starting doses. The review did not provide a good estimate of the incidence of harms associated with ARBs because of the short duration of the trials and the lack of reporting of adverse effects in many of the trials.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest declared.
Figures






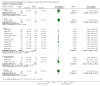




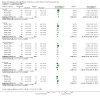









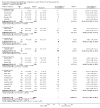
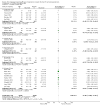







Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Andersson 1998 {published data only}
-
- Andersson OK, Neldam S. The antihypertensive effect and tolerability of candesartan cilexitil, a new generation angiotensin II antagonist, in comparison with losartan. Blood Pressure 1998;7(1):53‐9. - PubMed
Benetos 2000 {published data only}
-
- Benetos A, Gautier S, Lafleche A, Topouchian J, Frangin G, Girerd X, Sissmann J, Safar ME. Blockade of angiotensin II type 1 receptors: Effect on carotid and radial artery structure and function in hypertensive humans. Journal of Vascular Research 2000;37(1):8‐15. - PubMed
Benz 1998 {published data only}
-
- Benz JR, Black HR, Graff A, Reed A, Fitzsimmons S, Shi Y. Valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide in patients with essential hypertension. A multiple dose, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial comparing combination therapy with monotherapy. Journal of Human Hypertension 1998;12(12):861‐6. - PubMed
Black 1997 {published data only}
-
- Black HR, Graff A, Shute D, Stoltz R, Ruff D, Levine J, Shi Y, Mallows S. Valsartan, a new angiotensin II antagonist for the treatment of essential hypertension: efficacy, tolerability and safety compared to an angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor, lisinopril. Journal of Human Hypertension 1997;11(8):483‐9. - PubMed
Chrysant 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, Marbury TC, Robinson TD. Antihypertensive efficacy and safety of olmesartan medoxomil compared with amlodipine for mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 2003;17(6):425‐32. - PubMed
Chrysant 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, Weber MA, Wang AC, Hinman DJ. Evaluation of antihypertensive therapy with the combination of olmesartan medoxomil and hydrochlorothiazide. American Journal of Hypertension 2004;17(3):252‐9. - PubMed
Cushman 2002 {published data only}
Farsang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Farsang C, Kawecka‐Jaszcz K, Langan J, Maritz F, Zannad F. Antihypertensive effects and tolerability of candesartan cilexitil alone and in combination with amlodipine. Clinical Drug Investigation 2001;21(1):17‐23.
Feldman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Feldman R, Chattman MS, Lonigro A, Sievers RJ. Tasosartan in patients with essential hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, dose‐titration study. Advances in Therapy 1997;14(5):290‐303.
Flack 2001 {published data only}
-
- Flack JM, Saunders E, Gradman A, Kraus WE, Lester M, Pratt H, Alderman M, Green S, Vargas R, Espenshade M, Ceesay P, Alexander J, Goldberg A. Antihypertensive efficacy and safety of losartan alone and in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in adult african americans with mild to moderate hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 2001;23(8):1193‐208. - PubMed
Flack 2003 {published data only}
-
- Flack JM, Oparil S, Pratt JH, Roniker B, Garthwaite S, Kleiman JH, Yang Y, Krause SL, Workman D, Saunders E. Efficacy and tolerability of eplerenone and losartan in hypertensive black and white patients. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2003;41(7):1148‐55. - PubMed
Fogari 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fogari R, Ambrosoli S, Corradi L, Esposti ED, Mos L, Nami R, Nicrosini F, Pessina AC, Salvetti A, Vaccarella A, Zanchetti A, Martin A, Reeves RA. 24‐hour blood pressure control by once‐daily administration of irbesartan assessed by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Journal of Hypertension 1997;15(12 Pt 1):1511‐8. - PubMed
Fogari 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fogari R, Zoppi A, Malamani G, Marasi G, Pesce RM, Banderali A, Mugellini A. Effects of four angiotensin II‐receptor antagonists on fibrolysis in postemenopausal women with hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research 2001;62(1):68‐78.
Gradman 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gradman AH, Arcuri KE, Goldberg AI, Ikeda LS, Nelson EB, Snavely DB, Sweet CS. A randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, parallel study of various doses of losartan potassium compared with enalapril maleate in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 1995;25(6):1345‐50. - PubMed
Gradman 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gradman AH, Gray J, Maggiacomo F, Punzi H, White WB. Assessment of once‐daily eprosartan, an angiotensin II antagonist, in patients with systemic hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 1999;21(3):442‐53. - PubMed
Gradman 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, Lins RL, Nussberger J, Chiang Y, Bedigian MP. Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, provides dose‐dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebo‐like tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2005;111(8):1012‐8. - PubMed
Guthrie 1998 {published data only}
-
- Guthrie R, Saini R, Herman T, Pleskow W, Sprecher D, Collins G. Efficacy and tolerability of irbesartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, in primary hypertension. Clinical Drug Investigation 1998;15(3):217‐27.
Hanefeld 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hanefeld M, Abletshauser C. Effect of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist valsartan on lipid profile and glucose metabolism in patients with hypertension. Journal of International Medical Research 2001;29(4):270‐9. - PubMed
Hedner 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hedner T, Oparil S, Rasmussen K, Rapelli A, Gatlin M, Kobi P, Sullivan J, Oddou‐Stock P. A comparison of the angiotensin II antagonists valsartan and losartan in the treatment of essential hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1999;12(4 Pt 1):414‐7. - PubMed
Holwerda 1996 {published data only}
-
- Holwerda NJ, Fogari R, Angeli P, Porcellati C, Hereng C, Oddou‐Stock P, Heath R, Bodin F. Valsartan, a new angiotensin II antagonist for the treatment of essential hypertension: efficacy and safety compared with placebo and enalapril. Journal of Hypertension 1996;14(9):1147‐51. - PubMed
Ikeda 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ikeda LS, Harm SC, Arcuri KE, Goldberg AI, Sweet CS. Comparative antihypertensive effects of losartan 50 mg and losartan 50 mg titrated to 100 mg in patients with essential hypertension. Blood Pressure 1997;6(1):35‐43. - PubMed
Kassler‐Taub 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kassler‐Taub K, Littlejohn T, Elliott W, Ruddy T, Adler E. Comparative efficacy of two angiotensin II receptor antagonists, irbesartan and losartan, in mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1998;11(4 Pt 1):445‐53. - PubMed
Klingbeil 2002 {published data only}
-
- Klingbeil AU, John S, Schneider MP, Jacobi J, Handrock R, Schmieder RE. Effect of AT1 receptor blockade on endothelial function in essential hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 2003;16(2):123‐8. - PubMed
-
- Klingbeil AU, John S, Schneider MP, Jacobi J, Weidinger G, Schmieder RE. AT1‐receptor blockade improves augmentation index: a double‐blind, randomized, controlled study. Journal of Hypertension 2002;20(12):2423‐8. - PubMed
Kochar 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kochar M, Guthrie R, Triscari J, Kassler‐Taub K, Reeves RA. Matrix study of irbesartan with hydrochlorothiazide in mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1999;12(8 Pt 1):797‐805. - PubMed
Lacourciere 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lacourciere Y, Pool JL, Svetkey L, Gradman AH, Larochelle P, Champlain J, Smith WB. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter trial of four doses of tasosartan in patients with essential hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1998;11(4 Pt 1):454‐61. - PubMed
Mallion 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mallion JM, Siche JP, Lacourciere Y. ABPM comparison of the antihypertensive profiles of the selective angiotensin II receptor antagonists telmisartan and losartan in patients with mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1999;13(10):657‐64. - PubMed
Manolis 2004 {published data only}
-
- Manolis AJ, Reid JL, Zeeuw D, Murphy MB, Seewaldt‐Becker E, Koster J. Angiotensin II receptor antagonist telmisartan in isolated systolic hypertension (ARAMIS) study: efficacy and safety of telmisartan 20, 40 or 80 mg versus hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg or placebo. Journal of Hypertension 2004;22(5):1033‐7. - PubMed
McGill 2001 {published data only}
-
- McGill JB. Angiotensin II receptor antagonist plus a thiazide diuretic is more efficacious for treating hypertension than either drug alone. Blood Pressure Monitoring 2001;6(Suppl 1):S3‐S13.
-
- McGill JB, Reilly PA. Telmisartan plus hydrochlorothiazide versus telmisartan or hydrochlorothiazide monotherapy in patients with mild to moderate hypertension: A multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group trial. Clinical Therapeutics 2001;23(6):833‐50. - PubMed
Meineke 1997 {published data only}
-
- Meineke I, Feltkamp H, Hogemann A, Gundert‐Remy U. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of candesartan after administration of its pro‐drug candesartan cilexitil in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension ‐ a population analysis. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1997;53(3‐4):221‐8. - PubMed
Neutel 1998 {published data only}
-
- Neutel JM, Smith DHG. Dose response and antihypertensive efficacy of the AT1 receptor antagonist telmisartan in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Advances in Therapy 1998;15(4):206‐17.
Neutel 1999 {published data only}
-
- Neutel JM, Buckalew v, Chrysant SG, Mroczek WJ, Ruff DA, Weber M. Efficacy and tolerability of tasosartan, a novel angiotensin II receptor blocker: Results from a 10‐week, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐titration study. American Heart Journal 1999;137(1):118‐25. - PubMed
Neutel 2002 {published data only}
Oparil 1996 {published data only}
-
- Oparil S, Dyke S, Harris F, Kief J, James D, Hester A, Fitzsimmons S. The efficacy and safety of valsartan compared with placebo in the treatment of patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 1996;18(5):797‐810. - PubMed
Oparil 1999 {published data only}
-
- Oparil S. Eprosartan versus enalapril in hypertensive patients with angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor‐induced cough. Current Therapeutic Research 1999;60(1):1‐14.
Patterson 2003 {published data only}
Pool 1998 (study 1) {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Guthrie RM, Littlejohn TW, Raskin P, Shephard AMM, Weber MA, Weir MR, Wilson TW, Wright J, Kassler‐Taub KB, Reeves RA. Dose‐related antihypertensive effects of irbesartan in patients with mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1998;11(4 Pt 1):462‐70. - PubMed
Pool 1998 (study 2) {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Guthrie RM, Littlejohn TW, Raskin P, Shephard AMM, Weber MA, Weir MR, Wilson TW, Wright J, Kassler‐Taub KB, Reeves RA. Dose‐related antihypertensive effects of irbesartan in patients with mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1998;11(4 Pt 1):462‐70. - PubMed
Pool 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Glazer R, Chiang Y‐T, Gatlin M. Dose‐response efficacy of valsartan, a new angiotensin II receptor blocker. Journal of Human Hypertension 1999;13(4):275‐81. - PubMed
Punzi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Punzi HA, Punzi CF. Once‐daily eprosartan mesylate in the treatment of elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension: data from a 13‐week double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel, multicenter study. Journal of Human Hypertension 2004;18(9):655‐61. - PubMed
Reif 1998 {published data only}
-
- Reif M, White WB, Fagan TC, Oparil S, Flanagan TL, Edwards DT, Cushing DJ, Michelson EL. Effects of candesartan cilexitil in patients with systemic hypertension. American Journal of Cardiology 1998;82(8):961‐5. - PubMed
Schoenberger 1995 {published data only}
-
- Schoenberger JA. Losartan with hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1995;13(Suppl 1):S43‐S47. - PubMed
Smith 1998 {published data only}
-
- Smith DHG, Neutel JM, Morgenstern P. Once‐daily telmisartan compared with enalapril in the treatment of hypertension. Advances in Therapy 1998;15(4):229‐40.
Smith 2000 {published data only}
-
- Smith DHG, Matzek KM, Kempthorne‐Rawson J. Dose response and safety of telmisartan in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2000;40(12 Pt 1):1380‐90. - PubMed
Weber 1995 {published data only}
-
- Byyny RL. Antihypertensive efficacy of the angiotensin II AT1‐receptor antagonist losartan: results of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group trial using 24‐hour blood pressure monitoring. Blood Pressure 1996;5(Suppl 2):71‐7. - PubMed
-
- Byyny RL. Losartan potassium lowers blood pressure measured by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Journal of Hypertension 1995;13(Suppl 1):S29‐S33. - PubMed
-
- Weber MA, Byyny RL, Pratt JH, Faison EP, Snavely DB, Goldberg AI, Nelson EB. Blood pressure effects of the angiotensin II receptor blocker, losartan. Archives of Internal Medicine 1995;155(4):405‐11. - PubMed
-
- Weber MA, Neutel JM, Smith DHG. Controlling blood pressure throughout the day: issues in testing a new anti‐hypertensive agent. Journal of Human Hypertension 1995;9(Suppl 5):S29‐S35. - PubMed
White 2001 {published data only}
-
- White WB, Anwar YA, Mansoor GA, Sica DA. Evaluation of the 24‐hour blood pressure effects of eprosartan in patients with systemic hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 2001;14(12):1248‐55. - PubMed
White 2002 {published data only}
-
- White WB, Sica DA, Calhoun D, Mansoor GA, Anders RJ. Preventing increases in early‐morning blood pressure, heart rate, and the rate‐pressure product with controlled onset extended release verapamil at bedtime versus enalapril, losartan, and placebo on arising. American Heart Journal 2002;144(4):657‐65. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ABC 2000 {published data only}
-
- Association of Black Cardiologists (ABC) Candesartan Study Group. Evaluation of candesartan cilexetil in black patients with systemic hypertension: the ABC trial. Heart Disease 2000;2(6):392‐9. - PubMed
Asmar 2000 {published data only}
-
- Asmar R, Lacourciere Y. A new approach to assessing antihypertensive therapy: effect of treatment on pulse pressure. Journal of Hypertension 2000;18(11):1683‐90. - PubMed
-
- Lacourciere Y, Asmar R. A comparison of the efficacy and duration of action of candesartan cilexitil and losartan as assessed by clinic and ambulatory blood pressure after a missed dose, in truly hypertensive patients: a placebo‐controlled, forced titration study. American Journal of Hypertension 1999;12(12 Pt 1‐2):1181‐7. - PubMed
Asmar 2001 {published data only}
-
- Asmar R. Effect of telmisartan on arterial distensibility and central blood pressure in patients with mild to moderate hypertension and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System 2001;2(Suppl 2):S8‐11. - PubMed
Bakris 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bakris G, Sica D, Ram V, Fagan T, Vaitkus PT, Anders RJ, et al. A comparative trial of controlled‐onset, extended‐release verapamil, enalapril, and losartan on blood pressure and heart rate changes. American Journal of Hypertension 2002;15(1 Pt 1):53‐7. - PubMed
Fagard 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fagard R, Lijnen P, Pardaens K, Thijs L, Vinck W. A randomised, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, crossover study of losartan and enalapril in patients with essential hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 2001;15(3):161‐7. - PubMed
Fridman 1999 {published data only}
-
- Fridman K, Wysocki M, Friberg P, Andersson OK. Candesartan cilexetil and renal hemodynamics in hypertensive patients. American Journal of Hypertension 2000;13(9):1045‐8. - PubMed
-
- Fridman KU, Wysocki M, Friberg PR, Andersson OK. Candesartan cilexetil in hypertension: effects of six weeks' treatment on haemodynamics, baroreceptor sensitivity and the renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system. Blood Pressure 1999;8(4):242‐7. - PubMed
Hedner 1999a {published data only}
-
- Hedner T, Himmelmann A. The efficacy and tolerance of one or two daily doses of eprosartan in essential hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1999;17(1):129‐36. - PubMed
Koh 2004 {published data only}
-
- Koh KK, Chung WJ, Ahn JY, Han SH, Kang WC, Seo YH, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers reduce tissue factor activity and plasminogen activator inhibitor type‐1 antigen in hypertensive patients: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Atherosclerosis 2004;177(1):155‐60. - PubMed
-
- Koh KK, Han SH, Chung W‐J, Ahn JY, Jin DK, Kim HS, et al. Comparison of effects of losartan, irbesartan, and candesartan on flow‐mediated brachial artery dilation and on inflammatory and thrombolytic markers in patients with systemic hypertension. American Journal of Cardiology 2004;93(11):1432‐5. - PubMed
Lacourciere 1998a {published data only}
-
- Lacourciere Y, Lenis J, Orchard R, Lewanczuk R, Houde M, Pesant Y, et al. A comparison of the efficacies and duration of action of the angiotensin II receptor blockers telemisartan and amlodipine. Blood Pressure Monitoring 1998;3(5):295‐302. - PubMed
Lacourciere 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lacourciere Y. The incidence of cough:A comparison of lisinopril, placebo and telmisartan, a novel angiotensin II antagonist. International Journal of Clinical Practice 1999;53(2):99‐103. - PubMed
Marino 1999 {published data only}
-
- Marino MR, Langenbacher KM, Ford NF, Raymond RH, Manning J, Vesterqvist O, et al. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of irbesartan in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1999;4(2):67‐75. - PubMed
McInnes 1997 {published data only}
-
- McInnes GT, O'Kane KP, Jonker J, Roth J. The efficacy and tolerability of candesartan cilexetil in an elderly hypertensive population. Journal of Human Hypertension 1997;11(Suppl 2):S75‐80. - PubMed
Neutel 1997 {published data only}
-
- Neutel J, Weber M, Pool J, Smith D, Fitzsimmons S, Chiang YT, et al. Valsartan, a new angiotensin II antagonist: antihypertensive effects over 24 hours. Clinical Therapeutics 1997;19(3):447‐58. - PubMed
Neutel 2000 {published data only}
-
- Neutel JM, Bedigian MP. Efficacy of valsartan in patients aged > or =65 years with systolic hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 2000;22(8):961‐9. - PubMed
Petrov 2001 {published data only}
-
- Petrov VV, Fagard RH, Lijnen PJ. T‐lymphocyte and plasma angiotensin‐converting enzyme activity during enalapril and losartan administration in humans. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2001;38(4):578‐83. - PubMed
Zanchetti 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zanchetti A, Omboni S. Comparison of candesartan versus enalapril in essential hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 2001;14(2):129‐34. - PubMed
Zuschke 1999 {published data only}
-
- Zuschke CA, Keys I, Munger MA, Carr AA, Marinides GN, Flanagan TL, et al. Candesartan cilexitil: comparison of once‐daily versus twice‐daily administration for systemic hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 1999;21(3):464‐74. - PubMed
Additional references
Bucher 1997
-
- Bucher HC, Guyatt GH, Griffith LE, Walter D. The results of direct and indirect treatment comparisons in meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1997;50(6):683‐91. - PubMed
Cochrane Handbook
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D (editors). Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, Version 5.0.0 (updated February 2008).
e‐CPS
-
- e‐CPS [Internet]. Micardis [product monograph]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Pharmacists Association. Available from: http://www.e‐cps.ca. Also available in paper copy from the publisher, c2008 [updated 2005 May 4; cited 2008 Feb 29]:[product monograph].
Heran 2002
-
- Heran BS, Jauca CD, Wright JM. Development of an optimal search strategy for finding trials demonstrating ACE inhibitor blood pressure lowering efficacy. 10th International Cochran Colloquium, Stavenger, Norway 2002.
Jadad 1996
-
- 88.Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carrol D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Song 2003
WHO‐ICTRP
-
- World Health Organization. International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP). Available from: http://www.who.int/ictrp/en 2006 [cited 2008 Feb 29].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

