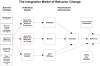
How sources of sexual information relate to adolescents' beliefs about sex
- PMID: 18844519
- PMCID: PMC2860278
- DOI: 10.5993/ajhb.33.1.4
How sources of sexual information relate to adolescents' beliefs about sex
Abstract
Objectives: To examine how sources of sexual information are associated with adolescents' behavioral, normative, and control beliefs about having sexual intercourse using the integrative model of behavior change.
Methods: Survey data from a quota sample of 459 youth.
Results: The most frequently reported sources were friends, teachers, mothers, and media. Regression analyses indicated that learning about sex from parents, grandparents, and religious leaders was associated with beliefs likely to delay sex; friends, cousins, and media were associated with beliefs that increase the likelihood of having sexual intercourse.
Conclusions: Different sexual information sources were associated with different underlying beliefs.
Figures
References
-
- Ward L. Understanding the role of entertainment media in the sexual socialization of American youth: a review of empirical research. Dev Rev. 2003;23:347–388.
-
- Brown JD, Keller SN. Can the mass media be healthy sex educators? Fam Plann Perspect. 2000 Sep-Oct;32(5):255–256. - PubMed
-
- Hoff T, Greene L, Davis J. National survey of adolescents and young adults: sexual health knowledge, attitudes, and experiences. Menlo Park, CA: Kaiser Family Foundation; 2003.
-
- Sutton MJ, Brown JD, Wilson KM, et al. Shaking the tree of knowledge for forbidden fruit: Where adolescents learn about sexuality and contraception. Brown
-
- Steele JDJR, Walsh-Childers K, editors. Sexual teens, sexual media: Investigating media’s influence on adolescent sexuality. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2002. pp. 25–57.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical