Regulation of Sp100A subnuclear localization and transcriptional function by EBNA-LP and interferon
- PMID: 18844582
- PMCID: PMC2988464
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2008.0023
Regulation of Sp100A subnuclear localization and transcriptional function by EBNA-LP and interferon
Abstract
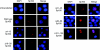
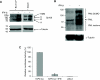
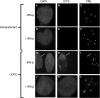
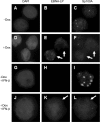
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) efficiently immortalizes human B cells and is associated with several human malignancies. The EBV transcriptional activating protein EBNA2 and the EBNA2 coactivator EBNA-leader protein (EBNA-LP) are important for B cell immortalization. Recent observations from our laboratory indicate that EBNA-LP coactivation function is mediated through interactions with the interferon-inducible gene (ISG) Sp100, resulting in displacement from its normal location in promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies (PML NBs) into the nucleoplasm. The EBNA-LP- and interferon-mediated mechanisms that regulate Sp100 subnuclear localization and transcriptional function remain undefined. To clarify these issues, we generated a panel of Sp100 mutant proteins to ascertain whether EBNA-LP induces Sp100 displacement from PML NBs by interfering with Sp100 dimerization or through other domains. In addition, we tested EBNA-LP function in interferon-treated cells. Our results indicate that Sp100 dimerization, PML NB localization, and EBNA-LP interaction domains overlap significantly. We also show that IFN-beta does not inhibit EBNA-LP coactivation function. The results suggest that EBNA-LP might play a role in EBV-evasion of IFN-mediated antiviral responses.
Figures




References
-
- Adams A. Lidin B. Strander H. Cantell K. Spontaneous interferon-production and Epstein-Barr virus antigen expression in human lymphoid-cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1975a;28:219–223. - PubMed
-
- Adams A. Strander H. Cantell K. Sensitivity of Epstein-Barr Virus transformed human lymphoid-cell lines to interferon. J Gen Virol. 1975b;28:207–217. - PubMed
-
- Ahn JH. Hayward GS. Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection. Virology. 2000;274:39–55. - PubMed
-
- Allday MJ. Crawford DH. Griffin BE. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene-expression during the initiation of B-cell immortalization. J Gen Virol. 1989;70:1755–1764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

