Mechanism of alcohol-induced oxidative stress and neuronal injury
- PMID: 18845238
- PMCID: PMC2605399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.08.030
Mechanism of alcohol-induced oxidative stress and neuronal injury
Abstract
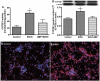
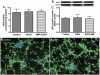
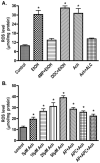
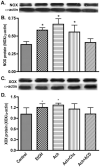
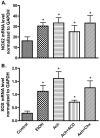
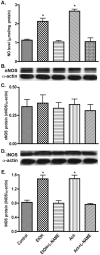
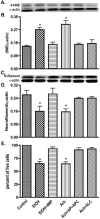
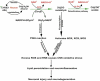
Neuro-cognitive deficits, neuronal injury, and neurodegeneration are well documented in alcoholics, yet the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Oxidative damage of mitochondria and cellular proteins intertwines with the progression of neuroinflammation and neurological disorders initiated by alcohol abuse. Here, we present the evidence that metabolism of ethanol in primary human neurons by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) or cytochrome P450-2E1 (CYP2E1) generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) via induction of NADPH/xanthine oxidase (NOX/XOX) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in human neurons. The acetaldehyde-mediated increase in NOX, XOX, or NOS activity is regulated as a transcriptional rather than a translational process. Marked increase in the lipid peroxidation product (4-hydroxynonenal) and enhanced ROS generation coincides with decreased neuronal viability and diminished expression of neuronal marker (neurofilaments). Novel quantitative methods of ROS and NO detection help dissect the mechanisms of alcohol-induced neurodegeneration. Uncovering the basic mechanisms of oxidative neuronal injury will serve as the basis for development of new therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Parsons OA. Neurocognitive deficits in alcoholics and social drinkers: a continuum? Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998;22:954–961. - PubMed
-
- Zeigler DW, Wang CC, Yoast RA, Dickinson BD, McCaffree MA, Robinowitz CB, et al. The neurocognitive effects of alcohol on adolescents and college students. Prev. Med. 2005;40:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Harper C. The neuropathology of alcohol-specific brain damage, or does alcohol damage the brain? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1998;57:101–110. - PubMed
-
- Lin MT, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443:787–795. - PubMed
-
- Maracchioni A, Totaro A, Angelini DF, Di Penta A, Bernardi G, Carri MT, et al. Mitochondrial damage modulates alternative splicing in neuronal cells: implications for neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2007;100:142–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

