Prenatal inflammation and lung development
- PMID: 18845493
- PMCID: PMC2652840
- DOI: 10.1016/j.siny.2008.08.011
Prenatal inflammation and lung development
Abstract
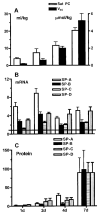
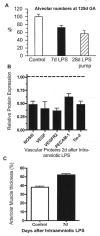
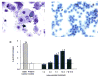
Prenatal exposure of very low birth weight infants to chronic indolent chorioamnionitis with organisms such as mycoplasma and ureaplasma is frequent. Chorioamnionitis is inconsistently associated with changed risks of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) or bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), probably because the diagnosis of chorioamnionitis does not quantify the extent or duration of the fetal exposures to infection and inflammation. The correlations between prenatal exposures and postnatal lung disease also are confounded by the imprecision of the diagnoses of RDS and BPD. In animal models, chorioamnionitis caused by pro-inflammatory mediators or live ureaplasma induces lung maturation, but also causes alveolar simplification and vascular injury. Intra-amniotic endotoxin administration also modulates the fetal innate immune system, resulting in maturation of monocytes to alveolar macrophages and the induction or paralysis of inflammatory responses depending on exposure history. Prenatal inflammation can have profound effects on the fetal lung and subsequent immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Charafeddine L, D'Angio CT, Phelps DL. Atypical chronic lung disease patterns in neonates. Pediatrics. 1999;103:759–65. - PubMed
-
- Preterm birth – causes, consequences and prevention. Institute of Medicine. Washington: National Academic Press; 2007.
-
- Romero R, Gomez R, Ghezzi F, et al. A fetal systemic inflammatory response is followed by the spontaneous onset of preterm parturition. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:186–93. - PubMed
-
- Perni SC, Vardhana S, Korneeva I, et al. Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum in midtrimester amniotic fluid: association with amniotic fluid cytokine levels and pregnancy outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191:1382–6. - PubMed
-
- Gerber S, Vial Y, Hohlfeld P, Witkin SS. Detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum in second-trimester amniotic fluid by polymerase chain reaction correlates with subsequent preterm labor and delivery. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:518–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

