The Year in Basic Science: nuclear receptors and coregulators
- PMID: 18845672
- PMCID: PMC5419400
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0297
The Year in Basic Science: nuclear receptors and coregulators
Abstract
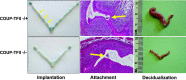
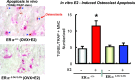
This article highlights the most significant scientific achievements of June 2007 to June 2008 in nuclear receptors (NRs) and coregulators. These molecules are the subjects of nine studies in three key areas of endocrinology: molecular endocrinology, endocrine metabolism, and endocrine pathology. In each case, the relevant NR or coregulator was found to play an integral role in the study, whether in elucidating a formerly unknown pathway or in initiating or facilitating a disease process. As more NRs and coregulators are researched, more therapeutic approaches to human disease can potentially be developed.
Figures





References
-
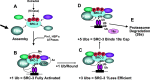
- Wu RC, Feng Q, Lonard DM, O'Malley BW 2007. SRC-3 coactivator functional lifetime is regulated by a phospho-dependent ubiquitin time clock. Cell 129:1125–1140 - PubMed
-
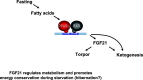
- Yin L, Wu N, Curtin JC, Qatanani M, Szwergold NR, Reid RA, Waitt GM, Parks DJ, Pearce KH, Wisely GB, Lazar MA 2007. Rev-erbα, a heme sensor that coordinates metabolic and circadian pathways. Science 318:1730–1731 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

