Genome-wide scan on total serum IgE levels identifies FCER1A as novel susceptibility locus
- PMID: 18846228
- PMCID: PMC2565692
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000166
Genome-wide scan on total serum IgE levels identifies FCER1A as novel susceptibility locus
Abstract
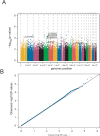
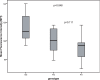
High levels of serum IgE are considered markers of parasite and helminth exposure. In addition, they are associated with allergic disorders, play a key role in anti-tumoral defence, and are crucial mediators of autoimmune diseases. Total IgE is a strongly heritable trait. In a genome-wide association study (GWAS), we tested 353,569 SNPs for association with serum IgE levels in 1,530 individuals from the population-based KORA S3/F3 study. Replication was performed in four independent population-based study samples (total n = 9,769 individuals). Functional variants in the gene encoding the alpha chain of the high affinity receptor for IgE (FCER1A) on chromosome 1q23 (rs2251746 and rs2427837) were strongly associated with total IgE levels in all cohorts with P values of 1.85 x 10(-20) and 7.08 x 10(-19) in a combined analysis, and in a post-hoc analysis showed additional associations with allergic sensitization (P = 7.78 x 10(-4) and P = 1.95 x 10(-3)). The "top" SNP significantly influenced the cell surface expression of FCER1A on basophils, and genome-wide expression profiles indicated an interesting novel regulatory mechanism of FCER1A expression via GATA-2. Polymorphisms within the RAD50 gene on chromosome 5q31 were consistently associated with IgE levels (P values 6.28 x 10(-7)-4.46 x 10(-8)) and increased the risk for atopic eczema and asthma. Furthermore, STAT6 was confirmed as susceptibility locus modulating IgE levels. In this first GWAS on total IgE FCER1A was identified and replicated as new susceptibility locus at which common genetic variation influences serum IgE levels. In addition, variants within the RAD50 gene might represent additional factors within cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 5q31, emphasizing the need for further investigations in this intriguing region. Our data furthermore confirm association of STAT6 variation with serum IgE levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Cooper PJ, Ayre G, Martin C, Rizzo JA, Ponte EV, et al. Geohelminth infections: a review of the role of IgE and assessment of potential risks of anti-IgE treatment. Allergy. 2008;63:409–417. - PubMed
-
- Gould HJ, Sutton BJ. IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:205–217. - PubMed
-
- Gould HJ, Mackay GA, Karagiannis SN, O'Toole CM, Marsh PJ, et al. Comparison of IgE and IgG antibody-dependent cytotoxicity in vitro and in a SCID mouse xenograft model of ovarian carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:3527–3537. - PubMed
-
- Dimson OG, Giudice GJ, Fu CL, Van den Bergh F, Warren SJ, et al. Identification of a potential effector function for IgE autoantibodies in the organ-specific autoimmune disease bullous pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;120:784–788. - PubMed
-
- Limb SL, Brown KC, Wood RA, Wise RA, Eggleston PA, et al. Adult asthma severity in individuals with a history of childhood asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:61–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

