Real-time, multidimensional in vivo imaging used to investigate blood flow in mouse pancreatic islets
- PMID: 18846254
- PMCID: PMC2564611
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI36209
Real-time, multidimensional in vivo imaging used to investigate blood flow in mouse pancreatic islets
Abstract
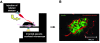
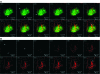
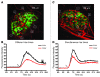
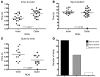
The pancreatic islets of Langerhans are highly vascularized micro-organs that play a key role in the regulation of blood glucose homeostasis. The specific arrangement of endocrine cell types in islets suggests a coupling between morphology and function within the islet. Here, we established a line-scanning confocal microscopy approach to examine the relationship between blood flow and islet cell type arrangement by real-time in vivo imaging of intra-islet blood flow in mice. These data were used to reconstruct the in vivo 3D architecture of the islet and time-resolved blood flow patterns throughout the islet vascular bed. The results revealed 2 predominant blood flow patterns in mouse islets: inner-to-outer, in which blood perfuses the core of beta cells before the islet perimeter of non-beta cells, and top-to-bottom, in which blood perfuses the islet from one side to the other regardless of cell type. Our approach included both millisecond temporal resolution and submicron spatial resolution, allowing for real-time imaging of islet blood flow within the living mouse, which has not to our knowledge been attainable by other methods.
Figures


References
-
- Svensson A.M., Ostenson C.G., Jansson L. Age-induced changes in pancreatic islet blood flow: evidence for an impaired regulation in diabetic GK rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000;279:E1139–E1144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK69603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK07563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD015052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR22620/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- EY08126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK68764/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK66636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR022620/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK53434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068764/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD15052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63439/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK063439/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

