Quantitative phosphoproteomics by mass spectrometry: past, present, and future
- PMID: 18846511
- PMCID: PMC2701620
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200800231
Quantitative phosphoproteomics by mass spectrometry: past, present, and future
Abstract
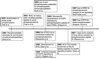
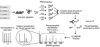
Protein phosphorylation-mediated signaling networks regulate much of the cellular response to external stimuli, and dysregulation in these networks has been linked to multiple disease states. Significant advancements have been made over the past decade to enable the analysis and quantification of cellular protein phosphorylation events, but comprehensive analysis of the phosphoproteome is still lacking, as is the ability to monitor signaling at the network level while comprehending the biological implications of each phosphorylation site. In this review we highlight many of the technological advances over the past decade and describe some of the latest applications of these tools to uncover signaling networks in a variety of biological settings. We finish with a concise discussion of the future of the field, including additional advances that are required to link protein phosphorylation analysis with biological insight.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hunter T. Signaling-2000 and beyond. Cell. 2000;100:113–127. - PubMed
-
- Seet BT, Dikic I, Zhou MM, Pawson T. Reading protein modifications with interaction domains. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:473–483. - PubMed
-
- Huang PH, Cavenee WK, Furnari FB, White FM. Uncovering therapeutic targets for glioblastoma: A systems biology approach. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:2750–2754. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T, Linding R. Network medicine. FEBS Lett. 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

