Persistent left superior vena cava: a case report and review of literature
- PMID: 18847480
- PMCID: PMC2576163
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-6-50
Persistent left superior vena cava: a case report and review of literature
Abstract
Persistent left superior vena cava is rare but important congenital vascular anomaly. It results when the left superior cardinal vein caudal to the innominate vein fails to regress. It is most commonly observed in isolation but can be associated with other cardiovascular abnormalities including atrial septal defect, bicuspid aortic valve, coarctation of aorta, coronary sinus ostial atresia, and cor triatriatum. The presence of PLSVC can render access to the right side of heart challenging via the left subclavian approach, which is a common site of access utilized when placing pacemakers and Swan-Ganz catheters. Incidental notation of a dilated coronary sinus on echocardiography should raise the suspicion of PLSVC. The diagnosis should be confirmed by saline contrast echocardiography.
Figures
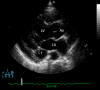

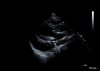

References
-
- Wood P. Disesase of heart and circulation. 2. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1956.
-
- Webb W, Gamsu G, Speckman J, Kaiser J, Federle M, Lipton M. Computed tomographic demonstration of mediastinal venous anomalies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982;139:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Voci P, Luzi G, Agati L. Diagnosis of persistent left superior vena cava by multiplane transesophageal echocardiography. Cardiologia. 1995;40:273–275. - PubMed
-
- Sarodia B, Stoller J. Persistent left superior vena cava: case report and literature review. Respir Care. 2000;45:411–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

