The adenosine deaminase inhibitor erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine decreases intestinal permeability and protects against experimental sepsis: a prospective, randomised laboratory investigation
- PMID: 18847498
- PMCID: PMC2592762
- DOI: 10.1186/cc7033
The adenosine deaminase inhibitor erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine decreases intestinal permeability and protects against experimental sepsis: a prospective, randomised laboratory investigation
Abstract
Introduction: The treatment of septic conditions in critically ill patients is still one of medicine's major challenges. Cyclic nucleotides, adenosine and its receptors play a pivotal role in the regulation of inflammatory responses and in limiting inflammatory tissue destruction. The aim of this study was to verify the hypothesis that adenosine deaminase-1 and cyclic guanosine monophosphate-stimulated phosphodiesterase inhibition by erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine could be beneficial in experimental endotoxicosis/sepsis.
Method: We used two established animal models for endotoxicosis and sepsis. Twenty-four male Wistar rats that had been given intravenous endotoxin (Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide) were treated with either erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine infusion or 0.9% saline during a study length of 120 minutes. Sepsis in 84 female C57BL/6 mice was induced by caecal ligation and puncture. Animals were treated with repeated erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine injections after 0, 12 and 24 hours or 4, 12 and 24 hours for delayed treatment.
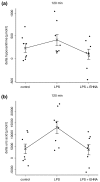
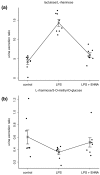
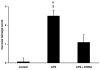
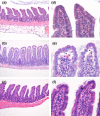
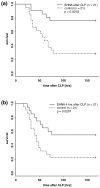
Results: In endotoxaemic rats, intestinal production of hypoxanthine increased from 9.8 +/- 90.2 micromol/l at baseline to 411.4 +/- 124.6 micromol/l and uric acid formation increased from 1.5 +/- 2.3 mmol/l to 13.1 +/- 2.7 mmol/l after 120 minutes. In endotoxaemic animals treated with erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine, we found no elevation of adenosine metabolites. The lactulose/L-rhamnose ratio (14.3 versus 4.2 in control animals; p = 2.5 x 10(-7)) reflects a highly permeable small intestine and through the application of erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine, intestinal permeability could be re-established. The lipopolysaccharide animals had decreased L-rhamnose/3-O-methyl-D-glucose urine excretion ratios. Erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine reduced this effect. The mucosa damage score of the septic animals was higher compared with control and therapy animals (p < 0.05). Septic shock induction by caecal ligation and puncture resulted in a 160-hour survival rate of about 25%. In contrast, direct adenosine deaminase-1 inhibition resulted in a survival rate of about 75% (p = 0.0018). A protective effect was still present when erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine treatment was delayed for four hours (55%, p = 0.029).
Conclusions: We present further evidence of the beneficial effects achieved by administering erythro-9-[2-hydroxyl-3-nonyl]-adenine, an adenosine deaminase-1 and cyclic guanosine monophosphate-stimulated phosphodiesterase inhibitor, in an endotoxicosis and sepsis animal model. This suggests a potential therapeutic option in the treatment of septic conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adenosine uptake and deamination regulate tonic A2a receptor facilitation of evoked [3H]acetylcholine release from the rat motor nerve terminals.Neuroscience. 1996 Jul;73(1):85-92. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(96)00028-0. Neuroscience. 1996. PMID: 8783232
-
Erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine inhibits cyclic-3',5'-guanosine monophosphate-stimulated phosphodiesterase to reverse hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in the perfused rat lung.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Feb;276(2):752-7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996. PMID: 8632346
-
Optimization of the local inhibition of intestinal adenosine deaminase (ADA) by erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine: enhanced oral delivery of an ADA-activated prodrug for anti-HIV therapy.J Pharm Sci. 1998 May;87(5):578-85. doi: 10.1021/js970377b. J Pharm Sci. 1998. PMID: 9572908
-
2-Aminopurine mutagenesis in Escherichia coli.Basic Life Sci. 1985;31:353-79. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2449-2_22. Basic Life Sci. 1985. PMID: 3888180 Review. No abstract available.
-
Can adenosine deaminase inhibitors be cytoprotective agents?Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;431:395-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5381-6_79. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 9598099 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Heterogeneity in Metabolic Responses to Dietary Fructose.Front Genet. 2019 Oct 31;10:945. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00945. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31737029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting target-ligand interactions with graph convolutional networks for interpretable pharmaceutical discovery.Sci Rep. 2022 May 19;12(1):8434. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12180-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35589824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parrillo JE, Parker MM, Natanson C, Suffredini AF, Danner RL, Cunnion RE, Ognibene FP. Septic shock in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis, cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Hynes-Gay P, Lalla P, Leo M, Merrill-Bell A, Nicholson M, Villaruel E. Understanding sepsis: from SIRS to septic shock. Dynamics. 2002;13:17–20. 22–24; quiz 25–26. - PubMed
-
- Lukashev D, Ohta A, Apasov S, Chen JF, Sitkovsky M. Cutting edge: physiologic attenuation of proinflammatory transcription by the Gs protein-coupled A2A adenosine receptor in vivo. J Immunol. 2004;173:21–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

