Use of flow cytometry to monitor Legionella viability
- PMID: 18849449
- PMCID: PMC2607165
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01364-08
Use of flow cytometry to monitor Legionella viability
Abstract
Legionella viability was monitored during heat shock treatment at 70 degrees C by a flow cytometric assay (FCA). After 30 min of treatment, for 6 of the 12 strains tested, the FCA still detected 10 to 25% of cells that were viable but nonculturable (VBNC). These VBNC cells were able to produce ATP and to be resuscitated after culture on amoebae.
Figures

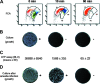
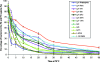
References
-
- AFNOR. 1993. Testing water-detection and enumeration of Legionella spp. and Legionella pneumophila—general method by direct culture and membrane filtration. French standard AFNOR NF T90-431. Association Française de Normalisation, Paris, France.
-
- Armisen, T. G., and P. Servais. 2004. Combining direct viable count (DVC) and fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH) to enumerate viable E. coli in rivers and wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 50:271-275. - PubMed
-
- Atlas, R. M. 1999. Legionella: from environmental habitats to disease pathology, detection and control. Environ. Microbiol. 1:283-293. - PubMed
-
- Barer, M. R., and C. R. Harwood. 1999. Bacterial viability and culturability. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 41:93-137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

