Male-pattern baldness susceptibility locus at 20p11
- PMID: 18849991
- PMCID: PMC2672151
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.255
Male-pattern baldness susceptibility locus at 20p11
Abstract
We conducted a genome-wide association study for androgenic alopecia in 1,125 men and identified a newly associated locus at chromosome 20p11.22, confirmed in three independent cohorts (n = 1,650; OR = 1.60, P = 1.1 x 10(-14) for rs1160312). The one man in seven who harbors risk alleles at both 20p11.22 and AR (encoding the androgen receptor) has a sevenfold-increased odds of androgenic alopecia (OR = 7.12, P = 3.7 x 10(-15)).
Figures
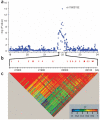
Comment in
-
Combing the genome for the root cause of baldness.Nat Genet. 2008 Nov;40(11):1270-1. doi: 10.1038/ng1108-1270. Nat Genet. 2008. PMID: 18957981 No abstract available.
-
Finding bald spots on chromosome 20p11.Clin Genet. 2009 Mar;75(3):226-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2009.01150_2.x. Clin Genet. 2009. PMID: 19250378 No abstract available.
References
-
- Olsen E. Disorders of hair growth: Diagnosis and Treatment. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1994. p. 257.
-
- Cash TF, Price VH, Savin RC. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1993;29:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Lo JC, et al. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006;91:1357–1363. - PubMed
-
- Nyholt DR, Gillespie NA, Heath AC, Martin NG. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2003;121:1561–1564. - PubMed
-
- Ellis JA, Stebbing M, Harrap SB. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2001;116:452–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

