Dif1 is a DNA-damage-regulated facilitator of nuclear import for ribonucleotide reductase
- PMID: 18851834
- PMCID: PMC3245869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.018
Dif1 is a DNA-damage-regulated facilitator of nuclear import for ribonucleotide reductase
Abstract
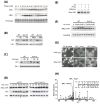
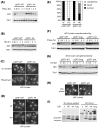
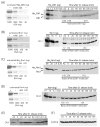
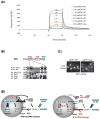
The control of dNTP concentrations is critical to the fidelity of DNA synthesis and repair. One level of regulation is through subcellular localization of ribonucleotide reductase. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the small subunit Rnr2-Rnr4 is nuclear, whereas the large subunit Rnr1 is cytoplasmic. In response to S phase or DNA damage, Rnr2-Rnr4 enters the cytoplasm to bind Rnr1, forming an active complex. We previously reported that Wtm1 anchors Rnr2-Rnr4 in the nucleus. Here, we identify DIF1, which regulates localization of Rnr2-Rnr4. Dif1 binds directly to the Rnr2-Rnr4 complex through a conserved Hug domain to drive nuclear import. Dif1 is both cell-cycle and DNA-damage regulated, the latter of which occurs via the Mec1-Dun1 pathway. In response to DNA damage, Dun1 directly phosphorylates Dif1, which both inactivates and degrades Dif1 and allows Rnr2-Rnr4 to become cytoplasmic. We propose that Rnr2-Rnr4 nuclear localization is achieved by a dynamic combination of Wtm1-mediated nuclear retention to limit export and regulated nuclear import through Dif1.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Yeast Dun1 Kinase Regulates Ribonucleotide Reductase Small Subunit Localization in Response to Iron Deficiency.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9807-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.720862. Epub 2016 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26970775 Free PMC article.
-
Control of ribonucleotide reductase localization through an anchoring mechanism involving Wtm1.Genes Dev. 2006 Feb 1;20(3):334-44. doi: 10.1101/gad.1380506. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16452505 Free PMC article.
-
Clb6-Cdc28 Promotes Ribonucleotide Reductase Subcellular Redistribution during S Phase.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Feb 27;38(6):e00497-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00497-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29263158 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage and cell cycle regulation of ribonucleotide reductase.Bioessays. 1993 May;15(5):333-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150507. Bioessays. 1993. PMID: 8343143 Review.
-
Rnr1's role in telomere elongation cannot be replaced by Rnr3: a role beyond dNTPs?Curr Genet. 2018 Jun;64(3):547-550. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0779-3. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29119271 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular basis of the essential s phase function of the rad53 checkpoint kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(16):3202-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00474-13. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23754745 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage response: three levels of DNA repair regulation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Aug 1;5(8):a012724. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012724. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23813586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast Dun1 kinase regulates ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1 in response to iron deficiency.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Sep;34(17):3259-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00472-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24958100 Free PMC article.
-
Hug1 is an intrinsically disordered protein that inhibits ribonucleotide reductase activity by directly binding Rnr2 subunit.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13174-85. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1095. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25378334 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Rrm2 gene dosage reduces fragile site breakage and prolongs survival of ATR mutant mice.Genes Dev. 2015 Apr 1;29(7):690-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.256958.114. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25838540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borgne A, Nurse P. The Spd1p S phase inhibitor can activate the DNA replication checkpoint pathway in fission yeast. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 23):4341–4350. - PubMed
-
- Chabes A, Domkin V, Thelander L. Yeast Sml1, a protein inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:36679–36683. - PubMed
-
- Chabes A, Georgieva B, Domkin V, Zhao X, Rothstein R, Thelander L. Survival of DNA damage in yeast directly depends on increased dNTP levels allowed by relaxed feedback inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase. Cell. 2003;112:391–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

