Implications of crosstalk between leptin and insulin signaling during the development of diet-induced obesity
- PMID: 18852044
- PMCID: PMC2713765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.09.005
Implications of crosstalk between leptin and insulin signaling during the development of diet-induced obesity
Abstract
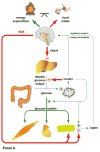
Insulin and leptin play complementary roles in regulating the consumption, uptake, oxidation and storage of nutrients. Chronic consumption of diets that contain a high proportion of calories from saturated fat induces a progressive deterioration in function of both hormones. Certain rat lines and strains of mice are particularly sensitive to the obesogenic and diabetogenic effects of high fat diets, and have been used extensively to study the developmental progression of insulin and leptin resistance in relation to the increasing adiposity that is characteristic of their response to these diets. Some aspects of the diminished efficacy of each hormone are secondary to increased adiposity but a consensus is emerging to support the view that direct effects of dietary components or their metabolites, independent of the resulting obesity, play important roles in development of insulin and leptin resistance. In this minireview, we will examine the implications of crosstalk between leptin and insulin signaling during the development of diet-induced obesity, emphasizing potential interactions between pathways that occur among target sites, and exploring how these interactions may influence the progression of obesity and diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- Surwit RS, Seldin MF, Kuhn CM, Cochrane C, Feinglos MN. Control of expression of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia by different genetic factors in diabetic C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes. 1991;40:82–87. - PubMed
-
- Surwit RS, Kuhn CM, Cochrane C, McCubbin JA, Feinglos MN. Diet-induced type II diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes. 1988;37:1163–1167. - PubMed
-
- Myers MG, Cowley MA, Munzberg H. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:537–556. - PubMed
-
- Park SY, Cho YR, Kim HJ, Higashimori T, Danton C, Lee MK, Dey A, Rothermel B, Kim YB, Kalinowski A, Russell KS, Kim JK. Unraveling the temporal pattern of diet-induced insulin resistance in individual organs and cardiac dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice. Diabetes. 2005;54:3530–3540. - PubMed
-
- Storlien LH, James DE, Burleigh KM, Chisholm DJ, Kraegen EW. Fat feeding causes widespread in vivo insulin resistance, decreased energy expenditure, and obesity in rats. Am J Physiol. 1986;251:E576–E583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 RR021945/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS051570/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01074772/PHS HHS/United States
- P20-RR021945/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AT002776/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50AT002776-01/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK074772/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM118430/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

