A model of evolution and structure for multiple sequence alignment
- PMID: 18852103
- PMCID: PMC2592536
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0170
A model of evolution and structure for multiple sequence alignment
Abstract
We have developed a phylogeny-aware progressive alignment method that recognizes insertions and deletions as distinct evolutionary events and thus avoids systematic errors created by traditional alignment methods. We now extend this method to simultaneously model regional heterogeneity and evolution. This novel method can be flexibly adapted to alignment of nucleotide or amino acid sequences evolving under processes that vary over genomic regions and, being fully probabilistic, provides an estimate of regional heterogeneity of the evolutionary process along the alignment and a measure of local reliability of the solution. Furthermore, the evolutionary modelling of substitution process permits adjusting the sensitivity and specificity of the alignment and, if high specificity is aimed at, leaving sequences unaligned when their divergence is beyond a meaningful detection of homology.
Figures

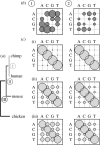
 ,
,  and
and  ), each alignment describing the ancestral node for the two nodes (extant or ancestral sequences) to be aligned. (b) The substitution process in each structure class is described by an instantaneous rate matrix Qi, here indicated by plots
), each alignment describing the ancestral node for the two nodes (extant or ancestral sequences) to be aligned. (b) The substitution process in each structure class is described by an instantaneous rate matrix Qi, here indicated by plots  and
and  showing the rates between different nucleotides as relative sizes of bubbles. In this example, structure classes 1 and 2 model regions of DNA sequence that evolve at the rate that is 150 and 50 per cent of the average rate, respectively. (c) For each pairwise alignment, indicated by different shades in the tree (a), substitution probability matrices for every structure class are computed from the corresponding matrix Qi. The evolutionary divergence between the sequence/ancestral node pairs to be aligned varies, as shown by the relative length of horizontal bars in the tree, and the alignments contain unequal amounts of information to distinguish the two evolutionary processes. (i) Between human and chimpanzee, both fast and slowly evolving regions (left and right matrix, respectively) are mostly conserved and the diagonal bubbles indicating no change are dominant. In the alignment of (ii) primate ancestor to mouse and (iii) mammalian ancestor to chicken, the fast evolving regions (left matrix) contain greater numbers of substitutions and the off-diagonal bubbles are relatively bigger.
showing the rates between different nucleotides as relative sizes of bubbles. In this example, structure classes 1 and 2 model regions of DNA sequence that evolve at the rate that is 150 and 50 per cent of the average rate, respectively. (c) For each pairwise alignment, indicated by different shades in the tree (a), substitution probability matrices for every structure class are computed from the corresponding matrix Qi. The evolutionary divergence between the sequence/ancestral node pairs to be aligned varies, as shown by the relative length of horizontal bars in the tree, and the alignments contain unequal amounts of information to distinguish the two evolutionary processes. (i) Between human and chimpanzee, both fast and slowly evolving regions (left and right matrix, respectively) are mostly conserved and the diagonal bubbles indicating no change are dominant. In the alignment of (ii) primate ancestor to mouse and (iii) mammalian ancestor to chicken, the fast evolving regions (left matrix) contain greater numbers of substitutions and the off-diagonal bubbles are relatively bigger.
Similar articles
-
Bayesian coestimation of phylogeny and sequence alignment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 1;6:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-83. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15804354 Free PMC article.
-
Indelign: a probabilistic framework for annotation of insertions and deletions in a multiple alignment.Bioinformatics. 2007 Feb 1;23(3):289-97. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl578. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17110370
-
Phylogeny-aware gap placement prevents errors in sequence alignment and evolutionary analysis.Science. 2008 Jun 20;320(5883):1632-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1158395. Science. 2008. PMID: 18566285
-
Homology assessment and molecular sequence alignment.J Biomed Inform. 2006 Feb;39(1):18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2005.11.005. Epub 2005 Dec 9. J Biomed Inform. 2006. PMID: 16380300 Review.
-
Tree disagreement: measuring and testing incongruence in phylogenies.J Biomed Inform. 2006 Feb;39(1):86-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2005.08.008. Epub 2005 Sep 28. J Biomed Inform. 2006. PMID: 16243006 Review.
Cited by
-
Linking genomics and ecology to investigate the complex evolution of an invasive Drosophila pest.Genome Biol Evol. 2013;5(4):745-57. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evt034. Genome Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23501831 Free PMC article.
-
webPRANK: a phylogeny-aware multiple sequence aligner with interactive alignment browser.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Nov 26;11:579. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-579. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 21110866 Free PMC article.
-
PhyloSim - Monte Carlo simulation of sequence evolution in the R statistical computing environment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Apr 19;12:104. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-104. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21504561 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the recombination landscape of hexaploid bread wheat reveals genes controlling recombination and gene conversion frequency.Genome Biol. 2019 Apr 15;20(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1675-6. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 30982471 Free PMC article.
-
Putting hornets on the genomic map.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 21;13(1):6232. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31932-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37085574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arribas-Gil, A., Metzler, D. & Plouhinec, J.-L. 2007 Statistical alignment with a sequence evolution model allowing rate heterogeneity along the sequence, IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform 29 Aug 2007, IEEE Computer Society Digital Library. (doi:10.1109/TCBB.2007.70246) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Durbin R, Eddy S, Krogh A, Mitchison G. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1998. Biological sequence analysis: probabilistic models of proteins and nucleic acids.
-
- Eddy S. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:755–763. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Edgar R, Sjölander K. SATCHMO: sequence alignment and tree construction using hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1404–1411. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg158 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gotoh O. An improved algorithm for matching biological sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1982;162:705–708. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(82)90398-9 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

