Polymorphism in the human major histocompatibility complex and early viral decline during treatment of chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 18852273
- PMCID: PMC2630649
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00947-08
Polymorphism in the human major histocompatibility complex and early viral decline during treatment of chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
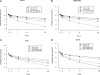
The dynamics of the viral decline immediately after the start of therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection may have prognostic potential for ultimate sustained virologic response. Considerable interindividual variability in the decline has been reported, including differences by race. The human major histocompatability complex (MHC) genes encode the human leukocyte antigens, which are important in the immune response to viral infections. We examined whether carriage of specific human MHC alleles are associated with the rate of the early viral decline. Longitudinal viral level data (baseline and days 1, 2, 7, 14, and 28 of treatment), medium resolution MHC genotyping, and random coefficients models were used to examine associations between MHC class I and class II allele carriage and the dynamics of the viral decline in 180 African-Americans (AAs) and 194 Caucasian Americans (CAs) with genotype-1 HCV infection over the first 28 days of treatment with peginterferon alpha2a plus ribavirin. Baseline viral levels were similar by race, irrespective of allele carriage. However, the rate of change in the viral decline was associated with both allele and race. Among the four subgroups defined by race and specific allele, the fastest rates of decline were observed (in terms of estimated mean viral declines log(10) IU/ml during the first four weeks) in CA noncarriers for A*03 (2.75; P = 0.018), in CA carriers for Cw*03 (2.99; P = 0.046), and in CA noncarriers for DQA1*04 (2.66; P = 0.018) or DQB1*0402 (2.65; P = 0.018). MHC alleles are associated with the viral decline during the first 28 days of peginterferon therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Aikawa, T., M. Kojima, H. Onishi, R. Tamura, S. Fukuda, T. Suzuki, F. Tsuda, H. Okamoto, Y. Miyakawa, and M. Mayumi. 1996. HLA DRB1 and DQB1 alleles and haplotypes influencing the progression of hepatitis C. J. Med. Virol. 49:274-278. - PubMed
-
- Alter, M., D. Kruszon-Moran, O. Nainan, G. McQuillan, F. Gao, L. Moyer, R. Kaslow, and H. Margolis. 1999. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N. Engl. J. Med. 341:556-562. - PubMed
-
- Bowen, D. G., and C. M. Walker. 2005. Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature 436:946-952. - PubMed
-
- Brown, H., and R. Prescott. 1999. Applied mixed models in medicine. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY.
-
- Conjeevaram, H. S., M. W. Fried, L. J. Jeffers, N. A. Terrault, T. E. Wiley-Lucas, N. Afdhal, R. S. Brown, S. H. Belle, J. H. Hoofnagle, D. E. Kleiner, and C. D. Howell. 2006. Peginterferon and ribavirin treatment in African American and Caucasian American patients with hepatitis C genotype 1. Gastroenterology 131:470-477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK60329/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1KL2 RR024154-02/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60344/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60342/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR16500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60309/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024154/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60352/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060342/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M02 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060352/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060335/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60335/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60346/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060309/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060344/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060346/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060340/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60340/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060329/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK60345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

