Characterization of pUO-StVR2, a virulence-resistance plasmid evolved from the pSLT virulence plasmid of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 18852276
- PMCID: PMC2592850
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00563-08
Characterization of pUO-StVR2, a virulence-resistance plasmid evolved from the pSLT virulence plasmid of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
pUO-StVR2 is a virulence-resistance plasmid which originated from pSLT of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium through acquisition of a complex resistance island, flanked by regions that provide a toxin-antitoxin system and an iron uptake system. The presence of resistance and virulence determinants on the same plasmid allows coselection of both properties, potentially increasing health risks.
Figures
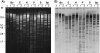
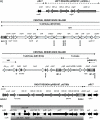
References
-
- Antunes, P., J. Machado, J. C. Sousa, and L. Peixe. 2004. Dissemination amongst humans and food products of animal origin of a Samonella typhimurium clone expressing an integron-borne OXA-30 β-lactamase. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 54:429-434. - PubMed
-
- Bances, M., A. Herrero, Y. González, M. R. Rodicio, and M. A. González-Hevia. 2007. Outbreak of gastroenteritis in a nursery school caused by a strain of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium carrying the hybrid virulence-resistance plasmid pUO-StVR2. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 25:376-381. - PubMed
-
- Boyd, D. A., and M. R. Mulvey. 2006. OXA-1 is OXA-30 is OXA-1. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58:224-225. - PubMed
-
- Braun, V. 2001. Iron uptake mechanisms and their regulation in pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 291:67-79. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. Y., G. W. Nace, B. Solow, and P. Fratamico. 2007. Complete nucleotide sequences of 84.5- and 3.2-kb plasmids in the multi-antibiotic resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium U302 strain G8430. Plasmid 57:29-43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

