Update on blepharospasm: report from the BEBRF International Workshop
- PMID: 18852443
- PMCID: PMC2676990
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000327601.46315.85
Update on blepharospasm: report from the BEBRF International Workshop
Abstract
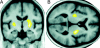
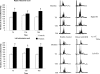
This review updates understanding and research on blepharospasm, a subtype of focal dystonia. Topics covered include clinical aspects, pathology, pathophysiology, animal models, dry eye, photophobia, epidemiology, genetics, and treatment. Blepharospasm should be differentiated from apraxia of eyelid opening. New insights into pathology and pathophysiology are derived from different types of imaging, including magnetic resonance studies. Physiologic studies indicate increased plasticity and trigeminal sensitization. While botulinum neurotoxin injections are the mainstay of therapy, other therapies are on the horizon.
Figures
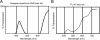
References
-
- Hallett M. Blepharospasm: recent advances. Neurology 2002;59:1306–1312. - PubMed
-
- Lamberti P, De Mari M, Zenzola A, Aniello MS, Defazio G. Frequency of apraxia of eyelid opening in the general population and in patients with extrapyramidal disorders. Neurol Sci 2002;23 suppl 2:S81–82. - PubMed
-
- Cakmur R, Ozturk V, Uzunel F, Donmez B, Idiman F. Comparison of preseptal and pretarsal injections of botulinum toxin in the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. J Neurol 2002;249:64–68. - PubMed
-
- Inoue K, Rogers JD. Botulinum toxin injection into Riolan’s muscle: somatosensory ‘trick.’ Eur Neurol 2007;58:138–141. - PubMed
-
- Kerty E, Eidal K. Apraxia of eyelid opening: clinical features and therapy. Eur J Ophthalmol 2006;16:204–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
