A prospective, randomized, double-blinded comparison of thymoglobulin versus Atgam for induction immunosuppressive therapy: 10-year results
- PMID: 18852661
- PMCID: PMC2695679
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318187bc67
A prospective, randomized, double-blinded comparison of thymoglobulin versus Atgam for induction immunosuppressive therapy: 10-year results
Abstract
Background: Use of induction for renal transplantation is controversial because of the concerns about long-term safety and efficacy.
Methods: We compared the safety and efficacy at 10 years among patients randomized to thymoglobulin or Atgam induction in a single center, randomized, double-blinded trial. Quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) were calculated using utility weights.
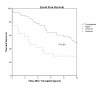
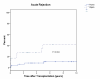
Results: The primary composite endpoint of freedom from death, graft loss, or rejection, "event-free survival," was higher with thymoglobulin compared with Atgam (48% vs. 29%; P=0.011). At 10 years, patient survival (75% vs. 67%) and graft survival (48% vs. 50%) were similar, whereas acute rejection remained lower (11% vs. 42%, P=0.004) in the thymoglobulin group. The incidence of all types of cancer was numerically lower with thymoglobulin compared with Atgam (8% vs. 21%, P=NS). There were no posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in the thymoglobulin group and there were two cases in the Atgam group. There were no new cases of cytomegalovirus disease in either group. Mean serum creatinine levels were higher (1.7+/-0.5 mg/dL vs. 1.2+/-0.3 mg/dL; P=0.003) and estimated glomerular filtration rates tended to be lower (49+/-22 mL/min vs. 65+/-19 mL/min; P=0.065) in the thymoglobulin group. There were 0.53 QALYs gained (3.68 thymoglobulin vs. 3.15 Atgam; 16.7% improvement) from thymoglobulin compared with Atgam.
Conclusions: This long-term follow-up showed that thymoglobulin was associated with higher event-free survival and improved QALYs, without increased posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder or cytomegalovirus disease, compared with Atgam at 10 years.
Figures
References
-
- Brennan DC, Flavin K, Lowell JA, et al. A randomized, double-blinded comparison of Thymoglobulin versus Atgam for induction immunosuppressive therapy in adult renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1999;67(7):1011. - PubMed
-
- Hardinger KL, Schnitzler MA, Miller B, et al. Five-year follow up of thymoglobulin versus ATGAM induction in adult renal transplantation. Transplantation. 2004;78(1):136. - PubMed
-
- Brennan DC, Garlock KA, Singer GG, et al. Prophylactic oral ganciclovir compared with deferred therapy for control of cytomegalovirus in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1997;64(12):1843. - PubMed
-
- Brennan DC, Garlock KA, Lippmann BA, et al. Control of cytomegalovirus-associated morbidity in renal transplant patients using intensive monitoring and either preemptive or deferred therapy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8(1):118. - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130(6):461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous