ROCK1 and LIMK2 interact in spread but not blebbing cancer cells
- PMID: 18852895
- PMCID: PMC2561063
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003398
ROCK1 and LIMK2 interact in spread but not blebbing cancer cells
Abstract
Cancer cells migrating within a 3D microenvironment are able to adopt either a mesenchymal or amoeboid mode of migration. Amoeboid migration is characterised by membrane blebbing that is dependent on the Rho effectors, ROCK1/2. We identify LIMK2 as the preferred substrate for ROCK1 but find that LIMK2 did not induce membrane blebbing, suggesting that a LIMK2 pathway is not involved in amoeboid-mode migration. In support of this hypothesis, novel FRET data demonstrate a direct interaction between ROCK1 and LIMK2 in polarised but not blebbing cells. Our results point to a specific role for the ROCK1:LIMK2 pathway in mesenchymal-mode migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

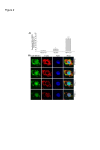
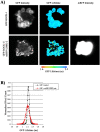
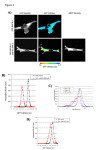
References
-
- Sahai E, Marshall CJ. RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:133–42. - PubMed
-
- Friedl P, Wolf K. Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:362–74. - PubMed
-
- Sahai E, Marshall CJ. Differing modes of tumour cell invasion have distinct requirements for Rho/ROCK signalling and extracellular proteolysis. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:711–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

