Squamozygomatic mastoiditis
- PMID: 18852992
- PMCID: PMC9442169
- DOI: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)30613-3
Squamozygomatic mastoiditis
Abstract
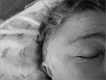
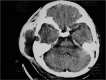
Acute atypical mastoiditis, with temporal and/or facial edema, is called squamozygomatic mastoiditis. There are only a few reports of this occurrence in the literature, which occurs because of an inflammatory process spread to the zygommatic apophysis, when mastoid pneumatization reaches the zygoma or the squamous portion of the temporal bone. Diagnosis is made based on clinical history, physical exam and mastoid CT scan. Treatment is carried out with antibiotic therapy and surgery.
Aim: To present a case of squamozygomatic mastoiditis and review the literature.
Patients and methods: Report of a case treated in our hospital during the year of 2003 and literature review through the Internet, we also reviewed otolaryngology books from known authors.
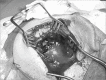
Discussion: Squamozygomatic mastoiditis is an atypical mastoiditis in which the inflammatory process spreads to the zygomatic apophysis. The infection reaches the temporal bone squamous portion and makes a fistula between this portion and the temporal muscle, shifting the pinna of the ear downwards and it may reach the face, eyes and eyelids. Diagnosis is carried out by clinical history, physical examination and mastoid CT Scan. Treatment is surgical, associated with antibiotic therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mastoiditis in children: a prospective, observational study comparing clinical presentation, microbiology, computed tomography, surgical findings and histology.Eur J Pediatr. 2008 May;167(5):541-8. doi: 10.1007/s00431-007-0549-1. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Eur J Pediatr. 2008. PMID: 17668240
-
Acute Mastoiditis Caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae.Pediatr Ann. 2016 May 1;45(5):e176-9. doi: 10.3928/00904481-20160328-01. Pediatr Ann. 2016. PMID: 27171806 Review.
-
Acute mastoiditis in children: Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a leading pathogen.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2003 Mar;67(3):277-81. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5876(02)00388-9. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2003. PMID: 12633928
-
Acute mastoiditis and osteomyelitis of the temporal bone.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005 Oct;69(10):1399-405. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2005.03.036. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005. PMID: 15935482
-
[Acute mastoiditis in children].Duodecim. 2014;130(3):251-7. Duodecim. 2014. PMID: 24660384 Review. Finnish.
References
-
- Castro JC. Mastoidite Aguda Tratado de Otorrinolaringologia - Sociedade Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia. 1a edição, Brasil. 2003;2:38–49.
-
- Tessa AH, Nalton FF, Reza R. Acute mastoiditis whit temporomandibular joint effusion. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;125:111–112. - PubMed
-
- Hungria - Complicações das Otites médias - Otorrinolaringologia. 7ª edição. 1995;38:342–350.
-
- Sharma SC. Complications of Otitis Media. Dep ENT Kathmandu Medical College.
Uncited Reference
-
- Butugan O, Santoro PP. Osteomielite frontal, Etmoidal e Temporal Tratado de Otorrinolaringologia - Sociedade Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia. 1a edição, Brasil. 2003;3:119–125.
-
- Warnaar A, Snoep G, Stals FSA. Swollen cheek, an unsual course of acute mastoiditis. Int J Ped Otorhinolaryngol. 1989;17:179–183. - PubMed
-
- Arts HA, Neely JG. Intratemporal and Intracranial Complications of Otitis Media. Byron J Bailey. Head Neck Surg Otolaryngol. Third Edition. 2;1759-77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

