Connexins, pannexins, innexins: novel roles of "hemi-channels"
- PMID: 18853183
- PMCID: PMC2656403
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-008-0591-5
Connexins, pannexins, innexins: novel roles of "hemi-channels"
Abstract
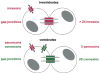
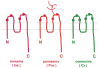
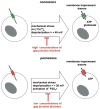
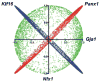
The advent of multicellular organisms, some 800 million years ago, necessitated the development of mechanisms for cell-to-cell synchronization and for the spread of signals across increasingly large cell populations [168, 185]. Many structures and mechanisms have evolved to achieve such functions [4, 15]. Among these mechanisms, one which is prominent in both the invertebrate and the vertebrate world, across the entire phylogenetic scale, involves the transmembrane flux of large cytosolic and extracellular molecules [, , , , –71, 121, 128, 129, 147, 154, 163]. These fluxes, in turn, are dependent on the formation of specific channels that in all animal classes are made by tetra-span integral membrane proteins [, , –71, 121, 128, 129, 147, 154, 163] (Fig. 1).
Figures
References
-
- Aleksic B, Ishihara R, Takahashi N, Maeno N, Ji X, Saito S, Inada T, Ozaki N. Gap junction coding genes and schizophrenia: a genetic association study. J Hum Genet. 2007;52:498–501. - PubMed
-
- Alves LA, Coutinho-Silva R, Persechini PM, Spray DC, Savino W, Campos de Carvalho AC. Are there functional gap junctions or junctional hemichannels in macrophages? Blood. 1996;88:328–334. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM. Ion channels and disease. Academic press; San Diego USA: 2000. p. 481.
-
- Azanza MJ, Pes N, Pérez-Bruzón RN, Aisa J, Raso M, Junquera C, Lahoz JM, Maestú C, Martínez-Ciriano C, Pérez-Castejón C, Vera-Gil A, Del Moral A. Localization of connexins in neurons and glia cells of the Helix aspersa suboesophageal brain ganglia by immunocytochemistry. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22:497–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

