Ligand-enhanced reactive oxidant generation by nanoparticulate zero-valent iron and oxygen
- PMID: 18853812
- PMCID: PMC2701397
- DOI: 10.1021/es801438f
Ligand-enhanced reactive oxidant generation by nanoparticulate zero-valent iron and oxygen
Abstract
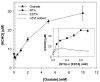
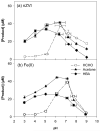
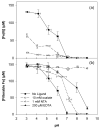
The reaction of zero-valent iron or ferrous iron with oxygen produces reactive oxidants capable of oxidizing organic compounds. However, the oxidant yield in the absence of ligands is too low for practical applications. The addition of oxalate, nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA), or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) to oxygen-containing solutions of nanoparticulate zero-valent iron (nZVI) significantly increases oxidant yield, with yields approaching their theoretical maxima near neutral pH. These ligands improve oxidant production by limiting iron precipitation and by accelerating the rates of key reactions, including ferrous iron oxidation by oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Product yields indicate that the oxic nZVI system produces hydroxyl radical (OH*) over the entire pH range in the presence of oxalate and NTA. In the presence of EDTA, probe compound oxidation is attributed to OH under acidic conditions and a mixture of OH* and ferryl ion (Fe[IV]) at circumneutral pH.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oxidant production from corrosion of nano- and microparticulate zero-valent iron in the presence of oxygen: a comparative study.J Hazard Mater. 2014 Jan 30;265:201-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.066. Epub 2013 Dec 7. J Hazard Mater. 2014. PMID: 24361799
-
Polyphosphate-enhanced production of reactive oxidants by nanoparticulate zero-valent iron and ferrous ion in the presence of oxygen: Yield and nature of oxidants.Water Res. 2015 Dec 1;86:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Water Res. 2015. PMID: 26093796
-
Factors affecting the yield of oxidants from the reaction of nanoparticulate zero-valent iron and oxygen.Environ Sci Technol. 2008 Feb 15;42(4):1262-7. doi: 10.1021/es7025664. Environ Sci Technol. 2008. PMID: 18351103
-
High-valent nonheme iron-oxo species in biomimetic oxidations.J Inorg Biochem. 2006 Apr;100(4):421-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2006.01.014. Epub 2006 Mar 13. J Inorg Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16530841 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI)-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs): Applications, Mechanisms, and Future Prospects.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;13(21):2830. doi: 10.3390/nano13212830. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37947676 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A study on the mechanism of oxidized quinoline removal from acid solutions based on persulfate-iron systems.RSC Adv. 2020 Mar 27;10(21):12504-12510. doi: 10.1039/c9ra10556e. eCollection 2020 Mar 24. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497624 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species-related activities of nano-iron metal and nano-iron oxides.J Food Drug Anal. 2014 Mar;22(1):86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.007. Epub 2014 Feb 5. J Food Drug Anal. 2014. PMID: 24673906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced refractory organics removal by sponge iron-coupled microbe technology: performance and underlying mechanism analysis.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2022 Jan;45(1):117-130. doi: 10.1007/s00449-021-02645-0. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2022. PMID: 34617132
-
Feasibility of a Heterogeneous Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Fenton-like Process for the Removal of Glyphosate from Water.Molecules. 2023 Feb 27;28(5):2214. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052214. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903460 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneously degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol and EDTA in aqueous solution by the bimetallic Cu-Fe/O₂ system.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Jan;22(2):1186-98. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3372-z. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25119276
References
-
- Leupin OX, Hug SJ. Oxidation and removal of arsenic(III) from aerated groundwater by filtration through sand and zero-valent iron. Water Res. 2005;39:1729–1740. - PubMed
-
- Joo SH, Feitz AJ, Waite TD. Oxidative degradation of the carbothioate herbicide, molinate, using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004;38:2242–2247. - PubMed
-
- Joo SH, Feitz AJ, Sedlak DL, Waite TD. Quantification of the oxidizing capacity of nanoparticulate zero-valent iron. Environ Sci. Technol. 2005;39:1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Noradoun C, Engelmann MD, McLaughlin M, Hutcheson R, Breen K, Paszczynski A, Cheng IF. Destruction of chlorinated phenols by dioxygen activation under aqueous room temperature and pressure conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003;42:5024–5030.
-
- Noradoun CE, Cheng IF. EDTA degradation induced by oxygen activation in a zerovalent iron/air/water system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005;39:7158–7163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

