Transcriptional regulation of subclass 5b fimbriae
- PMID: 18854044
- PMCID: PMC2579436
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-180
Transcriptional regulation of subclass 5b fimbriae
Abstract
Background: Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is a major cause of infant and child mortality in developing countries. This enteric pathogen causes profuse watery diarrhea by elaborating one or more enterotoxins that intoxicate eukaryotic cells and ultimately leads to a loss of water to the intestinal lumen. Virulence is also dependent upon fimbrial adhesins that facilitate colonization of the small intestine.
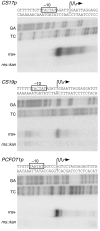
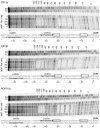
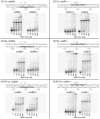
Results: The expression of CS1 fimbriae is positively regulated by Rns, a member of the AraC/XylS superfamily of transcriptional regulators. Based on fimbrial protein homology, CS1 fimbriae have been categorized as subclass 5b along with CS17, CS19, and PCFO71 fimbriae. In this study we show that Rns positively regulates the expression of these other subclass 5b members. DNase I footprinting revealed a Rns binding site adjacent to the -35 hexamer of each fimbrial promoter. The CS17 and PCFO71 fimbrial promoters carry a second Rns binding site centered at -109.5, relative to the Rns-dependent transcription start site. This second binding site is centered at -108.5 for the CS19 promoter. Mutagenesis of either site reduced Rns-dependent transcription from each promoter indicating that the molecules bound to these sites apparently function independently of one another, with each having an additive effect upon fimbrial promoter activation.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that the ETEC virulence regulator Rns is required for the expression of all known 5b fimbriae. Since Rns is also known to control the expression of additional ETEC fimbriae, including those within subclasses 5a and 5c, the inactivation or inhibition of Rns could be an effective strategy to prevent ETEC infections.
Figures

References
-
- Projections of Mortality and Burden of Disease http://www.who.int/healthinfo/statistics/bodprojections2030/en/index.html
-
- Richie E, Punjabi NH, Corwin A, Lesmana M, Rogayah I, Lebron C, Echeverria P, Simanjuntak CH. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea among young children in Jakarta, Indonesia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:85–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

