Nonclassic actions of vitamin D
- PMID: 18854395
- PMCID: PMC2630868
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2008-1454
Nonclassic actions of vitamin D
Abstract
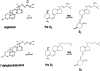
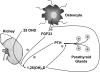
Context: Vitamin D receptors are found in most tissues, not just those participating in the classic actions of vitamin D such as bone, gut, and kidney. These nonclassic tissues are therefore potential targets for the active metabolite of vitamin D, 1,25(OH)(2)D. Furthermore, many of these tissues also contain the enzyme CYP27B1 capable of producing 1,25(OH)(2)D from the circulating form of vitamin D. This review was intended to highlight the actions of 1,25(OH)(2)D in several of these tissues but starts with a review of vitamin D production, metabolism, and molecular mechanism.
Evidence acquisition: Medline was searched for articles describing actions of 1,25(OH)(2)D on parathyroid hormone and insulin secretion, immune responses, keratinocytes, and cancer.
Evidence synthesis: Vitamin D production in the skin provides an efficient source of vitamin D. Subsequent metabolism to 1,25(OH)(2)D within nonrenal tissues differs from that in the kidney. Although vitamin D receptor mediates the actions of 1,25(OH)(2)D, regulation of transcriptional activity is cell specific. 1,25(OH)(2)D inhibits PTH secretion but promotes insulin secretion, inhibits adaptive immunity but promotes innate immunity, and inhibits cell proliferation but stimulates their differentiation.
Conclusions: The nonclassic actions of vitamin D are cell specific and provide a number of potential new clinical applications for 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) and its analogs. However, the use of vitamin D metabolites and analogs for these applications remains limited by the classic actions of vitamin D leading to hypercalcemia and hypercalcuria.
Figures
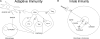
References
-
- Armas LA, Hollis BW, Heaney RP 2004 Vitamin D2 is much less effective than vitamin D3 in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5387–5391 - PubMed
-
- Romagnoli E, Mascia ML, Cipriani C, Fassino V, Mazzei F, D'Erasmo E, Carnevale V, Scillitani A, Minisola S 2008 Short and long-term variations in serum calciotropic hormones after a single very large dose of ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) or cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in the elderly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3015–3020 - PubMed
-
- Holick MF, MacLaughlin JA, Clark MB, Holick SA, Potts Jr JT, Anderson RR, Blank IH, Parrish JA, Elias P 1980 Photosynthesis of previtamin D3 in human skin and the physiologic consequences. Science 210:203–205 - PubMed
-
- Holick MF, MacLaughlin JA, Doppelt SH 1981 Regulation of cutaneous previtamin D3 photosynthesis in man: skin pigment is not an essential regulator. Science 211:590–593 - PubMed

