A PHD-polycomb repressive complex 2 triggers the epigenetic silencing of FLC during vernalization
- PMID: 18854416
- PMCID: PMC2579339
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808687105
A PHD-polycomb repressive complex 2 triggers the epigenetic silencing of FLC during vernalization
Abstract
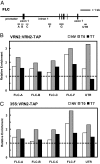
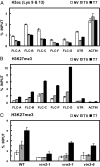
Vernalization, the acceleration of flowering by winter, involves cold-induced epigenetic silencing of Arabidopsis FLC. This process has been shown to require conserved Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) components including the Su(z)12 homologue, VRN2, and two plant homeodomain (PHD) finger proteins, VRN5 and VIN3. However, the sequence of events leading to FLC repression was unclear. Here we show that, contrary to expectations, VRN2 associates throughout the FLC locus independently of cold. The vernalization-induced silencing is triggered by the cold-dependent association of the PHD finger protein VRN5 to a specific domain in FLC intron 1, and this association is dependent on the cold-induced PHD protein VIN3. In plants returned to warm conditions, VRN5 distribution changes, and it associates more broadly over FLC, coincident with significant increases in H3K27me3. Biochemical purification of a VRN5 complex showed that during prolonged cold a PHD-PRC2 complex forms composed of core PRC2 components (VRN2, SWINGER [an E(Z) HMTase homologue], FIE [an ESC homologue], MSI1 [p55 homologue]), and three related PHD finger proteins, VRN5, VIN3, and VEL1. The PHD-PRC2 activity increases H3K27me3 throughout the locus to levels sufficient for stable silencing. Arabidopsis PHD-PRC2 thus seems to act similarly to Pcl-PRC2 of Drosophila and PHF1-PRC2 of mammals. These data show FLC silencing involves changed composition and dynamic redistribution of Polycomb complexes at different stages of the vernalization process, a mechanism with greater parallels to Polycomb silencing of certain mammalian loci than the classic Drosophila Polycomb targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schuettengruber B, Chourrout D, Vervoort M, Leblanc B, Cavalli G. Genome regulation by Polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell. 2007;128:735–745. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz YB, Pirrotta V. Polycomb complexes and epigenetic states. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:266–273. - PubMed
-
- Ringrose L. Polycomb comes of age: Genome-wide profiling of target sites. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:290–297. - PubMed
-
- Goodrich J, Tweedie S. Remembrance of things past: Chromatin remodeling in plant development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002;18:707–746. - PubMed
-
- Köhler C, Villar CBR. Programming of gene expression by Polycomb group proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18:236–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

