New insights on classification, identification, and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp
- PMID: 18854485
- PMCID: PMC2570156
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00022-08
New insights on classification, identification, and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp
Abstract
Blastocystis is an unusual enteric protozoan parasite of humans and many animals. It has a worldwide distribution and is often the most commonly isolated organism in parasitological surveys. The parasite has been described since the early 1900s, but only in the last decade or so have there been significant advances in our understanding of Blastocystis biology. However, the pleomorphic nature of the parasite and the lack of standardization in techniques have led to confusion and, in some cases, misinterpretation of data. This has hindered laboratory diagnosis and efforts to understand its mode of reproduction, life cycle, prevalence, and pathogenesis. Accumulating epidemiological, in vivo, and in vitro data strongly suggest that Blastocystis is a pathogen. Many genotypes exist in nature, and recent observations indicate that humans are, in reality, hosts to numerous zoonotic genotypes. Such genetic diversity has led to a suggestion that previously conflicting observations on the pathogenesis of Blastocystis are due to pathogenic and nonpathogenic genotypes. Recent epidemiological, animal infection, and in vitro host-Blastocystis interaction studies suggest that this may indeed be the case. This review focuses on such recent advances and also provides updates on laboratory and clinical aspects of Blastocystis spp.
Figures
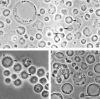
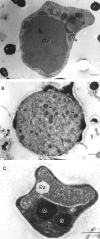
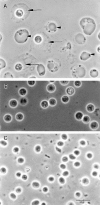
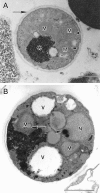
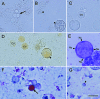
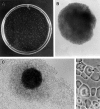
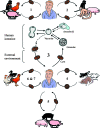
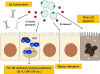
References
-
- Abe, N. 2004. Molecular and phylogenetic analysis of Blastocystis isolates from various hosts. Vet. Parasitol. 120:235-242. - PubMed
-
- Abe, N., Z. Wu, and H. Yoshikawa. 2003. Molecular characterization of Blastocystis isolates from birds by PCR with diagnostic primers and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene. Parasitol. Res. 89:393-396. - PubMed
-
- Abe, N., Z. Wu, and H. Yoshikawa. 2003. Molecular characterization of Blastocystis isolates from primates. Vet. Parasitol. 113:321-325. - PubMed
-
- Abe, N., Z. Wu, and H. Yoshikawa. 2003. Zoonotic genotypes of Blastocystis hominis detected in cattle and pigs by PCR with diagnostic primers and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene. Parasitol. Res. 90:124-128. - PubMed
-
- Abou El Naga, I. F., and A. Y. Negm. 2001. Morphology, histochemistry and infectivity of Blastocystis hominis cyst. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 31:627-635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

