Xq28 duplication presenting with intestinal and bladder dysfunction and a distinctive facial appearance
- PMID: 18854860
- PMCID: PMC2986219
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.192
Xq28 duplication presenting with intestinal and bladder dysfunction and a distinctive facial appearance
Abstract
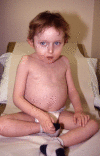
Xq28 duplications encompassing MECP2 have been described in male patients with a severe neurodevelopmental disorder associated with hypotonia and spasticity, severe learning disability and recurrent pneumonia. We identified an Xq28 duplication in three families where several male patients had presented with intestinal pseudo-obstruction or bladder distension. The affected boys had similar dysmorphic facial appearances. Subsequently, we ascertained seven further families where the proband presented with similar features. We demonstrated duplications of the Xq28 region in five of these additional families. In addition to MECP2, these duplications encompassed several other genes already known to be associated with diseases including SLC6A8, L1CAM and Filamin A (FLNA). The two remaining families were shown to have intragenic duplications of FLNA only. We discuss which elements of the Xq28 duplication phenotype may be associated with the various genes in the duplication. We propose that duplication of FLNA may contribute to the bowel and bladder phenotype seen in these seven families.
Figures


References
-
- Sanlaville D, Prieur M, de Blois M-C, et al. Functional disomy of the Xq28 chromosome region. Eur J Hum Genet. 2005;13:579–585. - PubMed
-
- Smyk M, Obersztyn E, Nowakowska B, et al. Different-sized duplications of Xq28, including MECP2, in three males with mental retardation, absent or delayed speech, and recurrent infections. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2008;147B:799–806. - PubMed
-
- Friez MJ, Jones JR, Clarkson K, et al. Recurrent infections, hypotonia, and mental retardation caused by duplication of MECP2 and adjacent region in Xq28. Pediatrics. 2006;118:e1687–e1695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

