Multiplex detection of protease activity with quantum dot nanosensors prepared by intein-mediated specific bioconjugation
- PMID: 18922019
- PMCID: PMC2677517
- DOI: 10.1021/ac801562f
Multiplex detection of protease activity with quantum dot nanosensors prepared by intein-mediated specific bioconjugation
Abstract
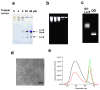
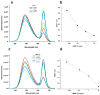
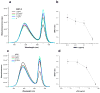
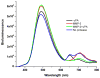
We report here a protease sensing nanoplatform based on semiconductor nanocrystals or quantum dots (QDs) and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (QD-BRET) to detect the protease activity in complex biological samples. These nanosensors consist of bioluminescent proteins as the BRET donor, quantum dots as the BRET acceptor, and protease substrates sandwiched between the two as a sensing group. An intein-mediated conjugation strategy was developed for site-specific conjugation of proteins to QDs in preparing these QD nanosensors. In this traceless ligation, the intein itself is spliced out and excluded from the final conjugation product. With this method, we have synthesized a series of QD nanosensors for highly sensitive detection of an important class of protease matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity. We demonstrated that these nanosensors can detect the MMP activity in buffers and in mouse serum with the sensitivity to a few nanograms per milliliter and secreted proteases by tumor cells. The suitability of these nanosensors for a multiplex protease assay has also been shown.
Figures


References
-
- Fingleton B. Front Biosci. 2006;11:479–491. - PubMed
-
- Egeblad M, Werb Z. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:161–174. - PubMed
-
- Brinckerhoff CE, Matrisian LM. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:207–214. - PubMed
-
- Bachmeier BE, Iancu CM, Jochum M, Nerlich AG. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2005;5:149–163. - PubMed
-
- Overall CM, Kleifeld O. Nature Rev Cancer. 2006;6:227–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

