The efficacy of topoisomerase II-targeted anticancer agents reflects the persistence of drug-induced cleavage complexes in cells
- PMID: 18922022
- PMCID: PMC2626429
- DOI: 10.1021/bi800981j
The efficacy of topoisomerase II-targeted anticancer agents reflects the persistence of drug-induced cleavage complexes in cells
Abstract
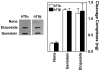
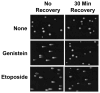
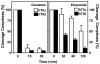
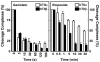
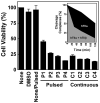
Genistein, a widely consumed bioflavonoid with chemopreventative properties in adults, and etoposide, a commonly prescribed anticancer drug, are well-characterized topoisomerase II poisons. Although both compounds display similar potencies against human topoisomerase IIalpha and IIbeta in vitro and induce comparable levels of DNA cleavage complexes in cultured human cells, their cytotoxic and genotoxic effects differ significantly. As determined by assays that monitored cell viability or the phosphorylation of histone H2AX, etoposide was much more toxic in CEM cells than genistein. Further studies that characterized the simultaneous treatment of cells with genistein and etoposide indicate that the differential actions of the two compounds are not related to the effects of genistein on cellular processes outside of its activity against topoisomerase II. Rather, they appear to result from a longer persistence of cleavage complexes induced by etoposide as compared to genistein. Parallel in vitro studies with purified type II enzymes led to similar conclusions regarding cleavage complex persistence. Isoform-specific differences were observed in vitro and in cells treated with etoposide. To this point, the t 1/2 of etoposide-induced DNA cleavage complexes formed with topoisomerase IIalpha in CEM cells was approximately 5 times longer than those formed with topoisomerase IIbeta. The cytotoxicity of etoposide following four treatment-recovery cycles was similar to that induced by continuous exposure to the drug over an equivalent time period. Taken together, these findings suggest that it may be possible to preferentially target topoisomerase IIalpha with etoposide by employing a schedule that utilizes pulsed drug treatment-recovery cycles.
Figures



References
-
- Berger JM, Gamblin SJ, Harrison SC, Wang JC. Structure and mechanism of DNA topoisomerase II. Nature. 1996;379:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Nitiss JL. Investigating the biological functions of DNA topoisomerases in eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1400:63–81. - PubMed
-
- Fortune JM, Osheroff N. Topoisomerase II as a target for anticancer drugs: When enzymes stop being nice. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2000;64:221–253. - PubMed
-
- Champoux JJ. DNA topisomerases: Structure, function, and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:369–413. - PubMed
-
- Wang JC. Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: A molecular perspective. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:430–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

