Functional analysis of phenylalanine residues in the active site of cytochrome P450 2C9
- PMID: 18922023
- PMCID: PMC2713172
- DOI: 10.1021/bi801231m
Functional analysis of phenylalanine residues in the active site of cytochrome P450 2C9
Abstract
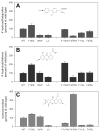
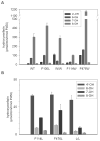
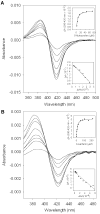
The two published crystal structures of cytochrome P450 2C9, complexed with ( S)-warfarin or flurbiprofen, implicate a cluster of three active site phenylalanine residues (F100, F114, F476) in ligand binding. However, these three residues appear to interact differently with these two ligands based on the static crystal structures. To elucidate the importance of CYP2C9's active site phenylalanines on substrate binding, orientation, and catalytic turnover, a series of leucine and tryptophan mutants were constructed and their interactions with ( S)-warfarin and ( S)-flurbiprofen examined. The F100-->L mutation had minor effects on substrate binding and metabolism of each substrate. In contrast, the F114L and F476L mutants exhibited substantially reduced ( S)-warfarin metabolism and altered hydroxy metabolite profiles but only modestly decreased nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) turnover while maintaining product regioselectivity. The F114-->W and F476-->W mutations also had opposing effects on ( S)-warfarin versus NSAID turnover. Notably, the F476W mutant increased the efficiency of ( S)-warfarin metabolism 5-fold, yet decreased the efficiency of ( S)-flurbiprofen turnover 20-fold. (1)H NMR T 1 relaxation studies suggested a slightly closer positioning of ( S)-warfarin to the heme in the F476W mutant relative to the wild-type enzyme, and stoichiometry studies indicated enhanced coupling of reducing equivalents to product formation for ( S)-warfarin, again in contrast to effects observed with ( S)-flurbiprofen. These data demonstrate that F114 and F476, but not F100, influence ( S)-warfarin's catalytic orientation. Differential interactions of F476 mutants with the two substrates suggest that their catalytically productive binding modes are not superimposable.
Figures
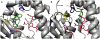
Similar articles
-
Enzymatic determinants of the substrate specificity of CYP2C9: role of B'-C loop residues in providing the pi-stacking anchor site for warfarin binding.Biochemistry. 1999 Mar 16;38(11):3285-92. doi: 10.1021/bi982161+. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10079071
-
CYP2C9 amino acid residues influencing phenytoin turnover and metabolite regio- and stereochemistry.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Jun;329(3):938-44. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.150706. Epub 2009 Mar 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19258521 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of human cytochrome P450 2C9 complexed with flurbiprofen at 2.0-A resolution.J Biol Chem. 2004 Aug 20;279(34):35630-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405427200. Epub 2004 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15181000
-
New insights into the structural features and functional relevance of human cytochrome P450 2C9. Part II.Curr Drug Metab. 2009 Dec;10(10):1127-50. doi: 10.2174/138920009790820101. Curr Drug Metab. 2009. PMID: 20167000 Review.
-
Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. doi: 10.2174/092986709789057635. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19515014 Review.
Cited by
-
Intramolecular heme ligation of the cytochrome P450 2C9 R108H mutant demonstrates pronounced conformational flexibility of the B-C loop region: implications for substrate binding.Biochemistry. 2010 Oct 12;49(40):8700-8. doi: 10.1021/bi100911q. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20815369 Free PMC article.
-
The relationships between cytochromes P450 and H2O2: Production, reaction, and inhibition.J Inorg Biochem. 2018 Sep;186:228-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 May 23. J Inorg Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29990746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preferred binding orientations of phenacetin in CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 are associated with isoform-selective metabolism.Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Dec;40(12):2324-31. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.047308. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012. PMID: 22949628 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and dynamics of the membrane-bound cytochrome P450 2C9.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Aug;7(8):e1002152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002152. Epub 2011 Aug 11. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21852944 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Expression and Functional Characterization of Novel CYP2C9 Variants Identified in the Alaska Native People.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020 Aug;374(2):233-240. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.265850. Epub 2020 May 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020. PMID: 32423989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rettie AE, Jones JP. Clinical and toxicological relevance of CYP2C9: drug-drug interactions and pharmacogenetics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;45:477–494. - PubMed
-
- Kirchheiner J, Brockmoller J. Clinical consequences of cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;77:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Wester MR, Yano JK, Schoch GA, Yang C, Griffin KJ, Stout CD, Johnson EF. The Structure of Human Cytochrome P450 2C9 Complexed with Flurbiprofen at 2.0-Å Resolution. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:35630–35637. - PubMed
-
- Williams PA, Cosme J, Ward A, Angove HC, Matak Vinković D, Jhoti H. Crystal structure of human cytochrome P450 2C9 with bound warfarin. Nature. 2003;424:464–468. - PubMed
-
- Johnson EF, Stout CD. Structural diversity of human xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;338:331–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

