NMR solution structure of the integral membrane enzyme DsbB: functional insights into DsbB-catalyzed disulfide bond formation
- PMID: 18922471
- PMCID: PMC2622435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.028
NMR solution structure of the integral membrane enzyme DsbB: functional insights into DsbB-catalyzed disulfide bond formation
Abstract
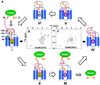
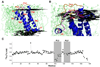
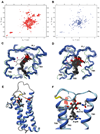
We describe the NMR structure of DsbB, a polytopic helical membrane protein. DsbB, a bacterial cytoplasmic membrane protein, plays a key role in disulfide bond formation. It reoxidizes DsbA, the periplasmic protein disulfide oxidant, using the oxidizing power of membrane-embedded quinones. We determined the structure of an interloop disulfide bond form of DsbB, an intermediate in catalysis. Analysis of the structure and interactions with substrates DsbA and quinone reveals functionally relevant changes induced by these substrates. Analysis of the structure, dynamics measurements, and NMR chemical shifts around the interloop disulfide bond suggest how electron movement from DsbA to quinone through DsbB is regulated and facilitated. Our results demonstrate the extraordinary utility of NMR for functional characterization of polytopic integral membrane proteins and provide insights into the mechanism of DsbB catalysis.
Figures



References
-
- Bader M, Muse W, Ballou DP, Gassner C, Bardwell JC. Oxidative protein folding is driven by the electron transport system. Cell. 1999;98:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Bardwell JC, McGovern K, Beckwith J. Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell. 1991;67:581–589. - PubMed
-
- Cierpicki T, Bushweller JH. Charged gels as orienting media for measurement of residual dipolar couplings in soluble and integral membrane proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:16259–16266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

