BDNF selectively regulates GABAA receptor transcription by activation of the JAK/STAT pathway
- PMID: 18922788
- PMCID: PMC2651003
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.1162396
BDNF selectively regulates GABAA receptor transcription by activation of the JAK/STAT pathway
Abstract
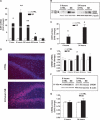
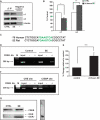
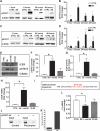
The gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) type A receptor (GABA(A)R) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor in the brain. Its multiple subunits show regional, developmental, and disease-related plasticity of expression; however, the regulatory networks controlling GABA(A)R subunit expression remain poorly understood. We report that the seizure-induced decrease in GABA(A)R alpha1 subunit expression associated with epilepsy is mediated by the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway regulated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNF- and seizure-dependent phosphorylation of STAT3 cause the adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP) response element-binding protein (CREB) family member ICER (inducible cAMP early repressor) to bind with phosphorylated CREB at the Gabra1:CRE site. JAK/STAT pathway inhibition prevents the seizure-induced decrease in GABA(A)R alpha1 abundance in vivo and, given that BDNF is known to increase the abundance of GABA(A)R alpha4 in a JAK/STAT-independent manner, indicates that BDNF acts through at least two distinct pathways to influence GABA(A)R-dependent synaptic inhibition.
Figures



References
-
- Rudolph U, Mohler H. GABA-based therapeutic approaches: GABAA receptor sub-type functions. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006;6:18–23. - PubMed
-
- Sieghart W. Structure, pharmacology, and function of GABAA receptor subtypes. Adv. Pharmacol. 2006;54:231–263. - PubMed
-
- Brooks-Kayal AR, Shumate MD, Jin H, Rikhter TY, Kelly ME, Coulter DA. gamma-Aminobutyric acid(A) receptor subunit expression predicts functional changes in hippocampal dentate granule cells during postnatal development. J. Neurochem. 2001;77:1266–1278. - PubMed
-
- Brooks-Kayal AR, Jin H, Price M, Dichter MA. Developmental expression of GABA(A) receptor subunit mRNAs in individual hippocampal neurons in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurochem. 1998;70:1017–1028. - PubMed
-
- Mohler H. Molecular recognition of cognitive functions and developmental plasticity: Impact of GABA(A) receptors. J. Neurochem. 2007;102:1–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

