Modulation of angiogenesis by a tetrameric tripeptide that antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1
- PMID: 18922791
- PMCID: PMC2590698
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806607200
Modulation of angiogenesis by a tetrameric tripeptide that antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1
Abstract
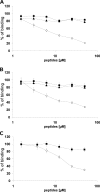
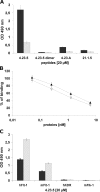
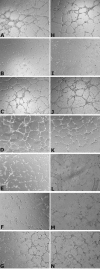
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1, also known as Flt-1) is involved in complex biological processes often associated to severe pathological conditions like cancer, inflammation, and metastasis formation. Consequently, the search for antagonists of Flt-1 has recently gained a growing interest. Here we report the identification of a tetrameric tripeptide from a combinatorial peptide library built using non-natural amino acids, which binds Flt-1 and inhibits in vitro its interaction with placental growth factor (PlGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) A and B (IC(50) approximately 10 microm). The peptide is stable in serum for 7 days and prevents both Flt-1 phosphorylation and the capillary-like tube formation of human primary endothelial cells stimulated by PlGF or VEGF-A. Conversely, the identified peptide does not interfere in VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 activation. In vivo, this peptide inhibits VEGF-A- and PlGF-induced neoangiogenesis in the chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane assay. In contrast, in the cornea, where avascularity is maintained by high levels of expression of the soluble form of Flt-1 receptor (sFlt-1) that prevents the VEGF-A activity, the peptide is able to stimulate corneal mouse neovascularization in physiological condition, as reported previously for others neutralizing anti-Flt-1 molecules. This tetrameric tripeptide represents a new, promising compound for therapeutic approaches in pathologies where Flt-1 activation plays a crucial role.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The biflavonoid amentoflavone inhibits neovascularization preventing the activity of proangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factors.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 3;286(22):19641-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.186239. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21471210 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-flt1 peptide, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1-specific hexapeptide, inhibits tumor growth and metastasis.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 1;11(7):2651-61. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1564. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15814646
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor and soluble FLT-1 receptor interactions and biological implications.Oncol Rep. 2005 Dec;14(6):1565-9. Oncol Rep. 2005. PMID: 16273257
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system: physiological functions in angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases.J Biochem. 2013 Jan;153(1):13-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvs136. Epub 2012 Nov 21. J Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23172303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placental growth factor (PlGF) and its receptor Flt-1 (VEGFR-1): novel therapeutic targets for angiogenic disorders.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Dec;979:80-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04870.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12543719 Review.
Cited by
-
The Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membrane as an In Vivo Assay to Study Antiangiogenesis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2010 Mar 8;3(3):482-513. doi: 10.3390/ph3030482. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2010. PMID: 27713265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics reveals ablation of PlGF increases antioxidant and neuroprotective proteins in the diabetic mouse retina.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 13;8(1):16728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34955-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30425286 Free PMC article.
-
The biflavonoid amentoflavone inhibits neovascularization preventing the activity of proangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factors.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 3;286(22):19641-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.186239. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21471210 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-B gene transfer exacerbates retinal and choroidal neovascularization and vasopermeability without promoting inflammation.Mol Vis. 2011 Feb 17;17:492-507. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21364963 Free PMC article.
-
Positive and Negative Regulation of Angiogenesis by Soluble Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 27;19(5):1306. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051306. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29702562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yancopoulos, G. D., Davis, S., Gale, N. W., Rudge, J. S., Wiegand, S. J., and Holash, J. (2000) Nature 407 242-248 - PubMed
-
- Olsson, A. K., Dimberg, A., Kreuger, J., and Claesson-Welsh, L. (2006) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7 359-371 - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet, P. (2005) Nature 438 932-936 - PubMed
-
- Ferrara, N., and Kerbel, R. S. (2005) Nature 438 967-974 - PubMed
-
- De Falco, S., Gigante, B., and Persico, M. G. (2002) Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 12 241-246 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

