Spirituality, social support, and survival in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 18922991
- PMCID: PMC2572290
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01790408
Spirituality, social support, and survival in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: No studies have evaluated the relationship among spirituality, social support, and survival in patients with ESRD. This study assessed whether spirituality was an independent predictor of survival in dialysis patients with ESRD after controlling for age, diabetes, albumin, and social support.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: A total of 166 patients who had ESRD and were treated with hemodialysis completed questionnaires on psychosocial variables, quality of life, and religious and spiritual beliefs. The religious variables were categorized into three scores on a 0 to 20 scale (low to high levels): Spirituality, religious involvement, and religion as coping. Social support was assessed using the Multidimensional Scale for Perceived Social Support. Analyses were also performed including and excluding patients with HIV infection. Religious variables were categorized on the basis of means, medians, and tertiles.
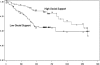
Results: In analyses that used religious variables, only the responses on the spirituality scale split at the mean were associated with survival. The association of other religious variables with survival did not reach significance. Social support correlated with spirituality, religion as coping, and religious involvement measures. Only social support and age were associated with survival when controlling for diabetes, albumin concentration, HIV infection, and spirituality.
Conclusions: These data suggest that the effects of spirituality may be mediated by social support. Larger, multicenter, prospective studies that use well-validated tools to measure religiosity and spirituality are needed to determine whether there is an independent association of spirituality variables with survival in patients with ESRD.
Figures

References
-
- Levin JS: How religion influences morbidity and health: Reflections on natural history, salutogenesis, and host resistance. Soc Sci Med 43: 849–864, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Koenig HG: Is Religion Good for your Health? New York, Haworth Press, 1997
-
- Ellison CG: Religious involvement and subjective well-being. J Health Soc Behav 32: 80–99, 1991 - PubMed
-
- Martin WT: Religiosity and United States suicide rates, 1972–1978. J Clin Psychol 40: 1166–1169, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Cornstock GW, Partridge KB: Church attendance and health. J Chronic Dis 24: 665–672, 1972 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

