Combined high serum ferritin and low iron saturation in hemodialysis patients: the role of inflammation
- PMID: 18922994
- PMCID: PMC2572292
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01070308
Combined high serum ferritin and low iron saturation in hemodialysis patients: the role of inflammation
Abstract
Background: Serum ferritin, frequently used as a marker of iron status in individuals with chronic kidney disease, is also an inflammatory marker. The concurrent combination of high serum ferritin and low iron saturation ratio (ISAT) usually poses a diagnostic dilemma. We hypothesized that serum ferritin > or =500 ng/ml, especially in the seemingly paradoxical presence of ISAT level <25%, is more strongly associated with inflammation than with iron in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients.
Design, setting, and participants: In 789 MHD patients in the Los Angeles area, the association of serum ferritin > or =500 ng/ml with inflammatory markers, including IL-6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein levels, and malnutrition-inflammation score (MIS) was examined.
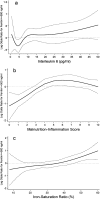
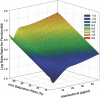
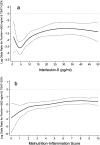
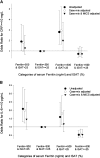
Results: After multivariate adjustment for case-mix and other measures of malnutrition-inflammation complex, MHD patients with serum ferritin > or =500 ng/ml and ISAT <25% had higher odds ratio for serum C-reactive protein > or =10 mg/L. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves for the continuum of ISAT and IL-6 in detecting a serum ferritin > or =500 ng/ml were identical (0.57 versus 0.56, P = 0.7). The combination of IL-6 with ISAT yielded a higher area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (0.61) than either ISAT or IL-6 alone (P = 0.03 and P = 0.02, respectively).
Conclusion: In MHD patients, ferritin values above 500 ng/ml, especially in paradoxical conjunction with low ISAT, are associated with inflammation. Strategies to dissociate inflammation from iron metabolism to mitigate the confounding impact of inflammation on iron and to improve iron treatment responsiveness may improve anemia management in chronic kidney disease.
Figures


References
-
- Regidor DL, Kopple JD, Kovesdy CP, Kilpatrick RD, McAllister CJ, Aronovitz J, Greenland S, Kalantar-Zadeh K: Associations between changes in hemoglobin and administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agent and survival in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1181–1191, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Van Wyck D, Eckardt KU, Uhlig K, Rocco M, Levin A: Appraisal of evidence and control of bias in the kidney disease outcomes quality initiative guideline development process. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2: 8–10, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Fishbane S, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Nissenson AR: Serum ferritin in chronic kidney disease: reconsidering the upper limit for iron treatment. Semin Dial 17: 336–341, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, McAllister CJ, Lehn RS, Lee GH, Nissenson AR, Kopple JD: Effect of malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome on EPO hyporesponsiveness in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 42: 761–773, 2003 - PubMed

