Dopaminergic suppression of brain deactivation responses during sequence learning
- PMID: 18923044
- PMCID: PMC4617653
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2933-08.2008
Dopaminergic suppression of brain deactivation responses during sequence learning
Abstract
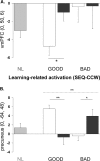
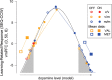
Cognitive processing is associated with deactivation of the default mode network. The presence of dopaminoceptive neurons in proximity to the medial prefrontal node of this network suggests that this neurotransmitter may modulate deactivation in this region. We therefore used positron emission tomography to measure cerebral blood flow in 15 Parkinson's disease (PD) patients while they performed a motor sequence learning task and a simple movement task. Scanning was conducted before and during intravenous levodopa infusion; the pace and extent of movement was controlled across tasks and treatment conditions. In normal and unmedicated PD patients, learning-related deactivation was present in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (p < 0.001). This response was absent in the treated condition. Treatment-mediated changes in deactivation correlated with baseline performance (p < 0.002) and with the val(158)met catechol-O-methyltransferase genotype. Our findings suggest that dopamine can influence prefrontal deactivation during learning, and that these changes are linked to baseline performance and genotype.
Figures



References
-
- Bates JF, Goldman-Rakic PS. Prefrontal connections of medial motor areas in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1993;336:211–228. - PubMed
-
- Bertolino A, Blasi G, Latorre V, Rubino V, Rampino A, Sinibaldi L, Caforio G, Petruzzella V, Pizzuti A, Scarabino T, Nardini M, Weinberger DR, Dallapiccola B. Additive effects of genetic variation in dopamine regulating genes on working memory cortical activity in human brain. J Neurosci. 2006;26:3918–3922. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertolino A, Di Giorgio A, Blasi G, Sambataro F, Caforio G, Sinibaldi L, Latorre V, Rampino A, Taurisano P, Fazio L, Romano R, Douzgou S, Popolizio T, Kolachana B, Nardini M, Weinberger DR, Dallapiccola B. Epistasis between dopamine regulating genes identifies a nonlinear response of the human hippocampus during memory tasks. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64:226–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
