Noradrenergic induction of odor-specific neural habituation and olfactory memories
- PMID: 18923046
- PMCID: PMC2588668
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3853-08.2008
Noradrenergic induction of odor-specific neural habituation and olfactory memories
Abstract
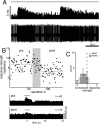
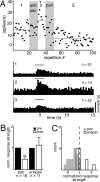
For many mammals, individual recognition of conspecifics relies on olfactory cues. Certain individual recognition memories are thought to be stored when conspecific odor cues coincide with surges of noradrenaline (NA) triggered by intensely arousing social events. Such familiar stimuli elicit reduced behavioral responses, a change likely related to NA-dependent plasticity in the olfactory bulb (OB). In addition to its role in these ethological memories, NA signaling in the OB appears to be relevant for the discrimination of more arbitrary odorants as well. Nonetheless, no NA-gated mechanism of long-term plasticity in the OB has ever been directly observed in vivo. Here, we report that NA release from locus ceruleus (LC), when coupled to odor presentation, acts locally in the main OB to cause a specific long-lasting suppression of responses to paired odors. These effects were observed for both food odors and urine, an important social recognition cue. Moreover, in subsequent behavioral tests, mice exhibited habituation to paired urine stimuli, suggesting that this LC-mediated olfactory neural plasticity, induced under anesthesia, can store an individual recognition memory that is observable after recovery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Noradrenergic neuromodulation in the olfactory bulb modulates odor habituation and spontaneous discrimination.Behav Neurosci. 2008 Aug;122(4):816-26. doi: 10.1037/a0012522. Behav Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18729635 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenergic inputs from the locus coeruleus to anterior piriform cortex and the olfactory bulb modulate olfactory outputs.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 2;16(1):260. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55609-9. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39747920 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenergic Activity in the Olfactory Bulb Is a Key Element for the Stability of Olfactory Memory.J Neurosci. 2020 Nov 25;40(48):9260-9271. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1769-20.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 23. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33097638 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical processing of odor objects.Neuron. 2011 Nov 17;72(4):506-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.027. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 22099455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Odor representation and coding by the mitral/tufted cells in the olfactory bulb.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024 Oct 15;25(10):824-840. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2400051. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024. PMID: 39420520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
α(1A)-Adrenergic regulation of inhibition in the olfactory bulb.J Physiol. 2013 Apr 1;591(7):1631-43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.248591. Epub 2012 Dec 24. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23266935 Free PMC article.
-
The neurobiology of safety and threat learning in infancy.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017 Sep;143:49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.10.015. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 27826033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stressors impair odor recognition memory via an olfactory bulb-dependent noradrenergic mechanism.Front Integr Neurosci. 2013 Dec 23;7:97. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2013.00097. eCollection 2013. Front Integr Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24391558 Free PMC article.
-
All in a sniff: olfaction as a model for active sensing.Neuron. 2011 Sep 22;71(6):962-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.030. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 21943596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABAB Receptors Tune Cortical Feedback to the Olfactory Bulb.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 10;36(32):8289-304. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3823-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27511004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams LM, Foote SL. Effects of locally infused pharmacological agents on spontaneous and sensory-evoked activity of locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res Bull. 1988;21:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Cohen JD. An integrative theory of locus coeruleus-norepinephrine function: adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:403–450. - PubMed
-
- Berridge CW, Abercrombie ED. Relationship between locus coeruleus discharge rates and rates of norepinephrine release within neocortex as assessed by in vivo microdialysis. Neuroscience. 1999;93:1263–1270. - PubMed
-
- Berridge CW, Waterhouse BD. The locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system: modulation of behavioral state and state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2003;42:33–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
