Huntingtin modulates transcription, occupies gene promoters in vivo, and binds directly to DNA in a polyglutamine-dependent manner
- PMID: 18923047
- PMCID: PMC2586288
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2126-08.2008
Huntingtin modulates transcription, occupies gene promoters in vivo, and binds directly to DNA in a polyglutamine-dependent manner
Abstract
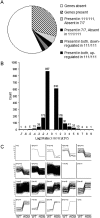
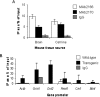
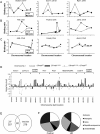
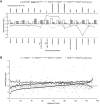
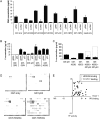
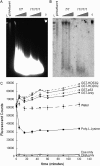
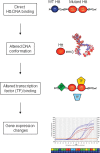
Transcriptional dysregulation is a central pathogenic mechanism in Huntington's disease, a fatal neurodegenerative disorder associated with polyglutamine (polyQ) expansion in the huntingtin (Htt) protein. In this study, we show that mutant Htt alters the normal expression of specific mRNA species at least partly by disrupting the binding activities of many transcription factors which govern the expression of the dysregulated mRNA species. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) demonstrates Htt occupation of gene promoters in vivo in a polyQ-dependent manner, and furthermore, ChIP-on-chip and ChIP subcloning reveal that wild-type and mutant Htt exhibit differential genomic distributions. Exon 1 Htt binds DNA directly in the absence of other proteins and alters DNA conformation. PolyQ expansion increases Htt-DNA interactions, with binding to recognition elements of transcription factors whose function is altered in HD. Together, these findings suggest mutant Htt modulates gene expression through abnormal interactions with genomic DNA, altering DNA conformation and transcription factor binding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson AN, Roncaroli F, Hodges A, Deprez M, Turkheimer FE. Chromosomal profiles of gene expression in Huntington's disease. Brain. 2008;131:381–388. - PubMed
-
- Bates GP, Harper PS, Jones AL. In: Huntington's Disease. Ed 3. Bates GP, Harper PS, Jones AL, editors. Oxford: Oxford UP; 2002.
-
- Benn CL, Landles C, Li H, Strand AD, Woodman B, Sathasivam K, Li SH, Ghazi-Noori S, Hockly E, Faruque SM, Cha JH, Sharpe PT, Olson JM, Li XJ, Bates GP. Contribution of nuclear and extranuclear polyQ to neurological phenotypes in mouse models of Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:3065–3078. - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, Lee TI, Levine SS, Wernig M, Tajonar A, Ray MK, Bell GW, Otte AP, Vidal M, Gifford DK, Young RA, Jaenisch R. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Callewaert L, Christiaens V, Haelens A, Verrijdt G, Verhoeven G, Claessens F. Implications of a polyglutamine tract in the function of the human androgen receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;306:46–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
