Meta-analysis of the symptom structure of obsessive-compulsive disorder
- PMID: 18923068
- PMCID: PMC3972003
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.08020320
Meta-analysis of the symptom structure of obsessive-compulsive disorder
Abstract
Objective: OCD is a clinically heterogeneous condition. This heterogeneity has the potential to reduce power in genetic, neuroimaging, and clinical trials. Despite a mounting number of studies, there remains debate regarding the exact factor structure of OCD symptoms. The authors conducted a meta-analysis to determine the factor structure of the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale Symptom Checklist.
Method: Studies were included if they involved subjects with OCD and included an exploratory factor analysis of the 13 Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale Symptom Checklist categories or the items therein. A varimax-rotation was conducted in SAS 9.1 using the PROC FACTOR CORR to extract factors from sample-size weighted co-occurrence matrices. Stratified meta-analysis was conducted to determine the factor structure of OCD in studies involving children and adults separately.
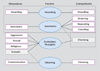
Results: Twenty-one studies involving 5,124 participants were included. The four factors generated were 1) symmetry: symmetry obsessions and repeating, ordering, and counting compulsions; 2) forbidden thoughts: aggression, sexual, religious, and somatic obsessions and checking compulsions, 3) cleaning: cleaning and contamination, and 4) hoarding: hoarding obsessions and compulsions. Factor analysis of studies including adults yielded an identical factor structure compared to the overall meta-analysis. Factor analysis of child-only studies differed in that checking loaded highest on the symmetry factor and somatic obsessions, on the cleaning factor.
Conclusions: A four-factor structure explained a large proportion of the heterogeneity in the clinical symptoms of OCD. Further item-level factor analyses are needed to determine the appropriate placement of miscellaneous somatic and checking OCD symptoms.
Figures
Comment in
-
Using individual items to clarify OCD symptom structure: the case for five factors.Am J Psychiatry. 2009 Jun;166(6):728-9; author reply 729-31. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09020287. Am J Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19487406 No abstract available.
References
-
- Karno M, Golding JM, Sorenson SB, Burnam MA. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in five US communities. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988;45:1094–1099. - PubMed
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Valleni-Basile LA, Garrison CZ, Jackson KL, Waller JL, McKeown RE, Addy CL, Cuffe SP. Frequency of obsessive-compulsive disorder in a community sample of young adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1994;33:782–791. - PubMed
-
- Mataix-Cols D, Rosario-Campos MC, Leckman JF. A multidimensional model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162:228–238. - PubMed
-
- Mataix-Cols D, Pertusa A, Leckman JF. Issues for DSM-V how should obsessive-compulsive and related disorders be classified? Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:1313–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

