Myc's broad reach
- PMID: 18923074
- PMCID: PMC2751281
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1712408
Myc's broad reach
Abstract
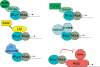
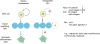
The role of the myc gene family in the biology of normal and cancer cells has been intensively studied since the early 1980s. myc genes, responding to diverse external and internal signals, express transcription factors (c-, N-, and L-Myc) that heterodimerize with Max, bind DNA, and modulate expression of a specific set of target genes. Over the last few years, expression profiling, genomic binding studies, and genetic analyses in mammals and Drosophila have led to an expanded view of Myc function. This review is focused on two major aspects of Myc: the nature of the genes and pathways that are targeted by Myc, and the role of Myc in stem cell and cancer biology.
Figures

References
-
- Adhikary S., Eilers M. Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;6:635–645. - PubMed
-
- Adhikary S., Marinoni F., Hock A., Hulleman E., Popov N., Beier R., Bernard S., Quarto M., Capra M., Goettig S., et al. The ubiquitin ligase HectH9 regulates transcriptional activation by Myc and is essential for tumor cell proliferation. Cell. 2005;123:409–421. - PubMed
-
- Arabi A., Rustum C., Hallberg E., Wright A.P. Accumulation of c-Myc and proteasomes at the nucleoli of cells containing elevated c-Myc protein levels. J. Cell Sci. 2003;116:1707–1717. - PubMed
-
- Arabi A., Wu S., Shiue C., Ridderstrale K., Larsson L.-G., Wright A.P.H. c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA in the nucleolus and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005;7:303–310. - PubMed
-
- Arnold I., Watt F.M. c-Myc activation in transgenic mouse epidermis results in mobilization of stem cells and differentiation of their progeny. Curr. Biol. 2001;11:558–568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
