Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function
- PMID: 18923184
- PMCID: PMC2899688
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00034.2007
Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function
Abstract
Protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms comprise a family of lipid-activated enzymes that have been implicated in a wide range of cellular functions. PKCs are modular enzymes comprised of a regulatory domain (that contains the membrane-targeting motifs that respond to lipid cofactors, and in the case of some PKCs calcium) and a relatively conserved catalytic domain that binds ATP and substrates. These enzymes are coexpressed and respond to similar stimulatory agonists in many cell types. However, there is growing evidence that individual PKC isoforms subserve unique (and in some cases opposing) functions in cells, at least in part as a result of isoform-specific subcellular compartmentalization patterns, protein-protein interactions, and posttranslational modifications that influence catalytic function. This review focuses on the structural basis for differences in lipid cofactor responsiveness for individual PKC isoforms, the regulatory phosphorylations that control the normal maturation, activation, signaling function, and downregulation of these enzymes, and the intra-/intermolecular interactions that control PKC isoform activation and subcellular targeting in cells. A detailed understanding of the unique molecular features that underlie isoform-specific posttranslational modification patterns, protein-protein interactions, and subcellular targeting (i.e., that impart functional specificity) should provide the basis for the design of novel PKC isoform-specific activator or inhibitor compounds that can achieve therapeutically useful changes in PKC signaling in cells.
Figures
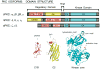







References
-
- Aces P, Beheshti M, Szallasi Z, Li L, Yuspa SH, Blumberg PM. Effect of a tyrosine 155 to phenylalanine mutation of protein kinase C-δ on the proliferative and tumorigenic properties of NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:887–891. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR. The protein kinase C inhibitors Ro 318220 and GF 109203X are equally potent inhibitors of MAPKAP kinase-1β (Rsk-2) and p70 S6 kinase. FEBS Lett. 1997;402:121–123. - PubMed
-
- Ananthanarayanan B, Stahelin RV, Digman MA, Cho W. Activation mechanisms of conventional protein kinase C isoforms are determined by the ligand affinity and conformational flexibility of their C1 domains. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:46886–46894. - PubMed
-
- Arimoto T, Takeishi Y, Takahashi H, Shishido T, Niizeki T, Koyama Y, Shiga R, Nozaki N, Nakajima O, Nishimaru K, Abe J, Endoh M, Walsh RA, Goto K, Kubota I. Cardiac-specific overexpression of diacylglycerol kinase-ζ prevents Gq protein-coupled receptor agonist-induced cardiac hypertrophy in transgenic mice. Circulation. 2006;113:60–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

