VEGF-A splicing: the key to anti-angiogenic therapeutics?
- PMID: 18923433
- PMCID: PMC2613352
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc2505
VEGF-A splicing: the key to anti-angiogenic therapeutics?
Abstract
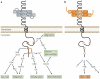
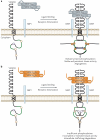
The physiology of microvessels limits the growth and development of tumours. Tumours gain nutrients and excrete waste through growth-associated microvessels. New anticancer therapies target this microvasculature by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) splice isoforms that promote microvessel growth. However, certain VEGF-A splice isoforms in normal tissues inhibit growth of microvessels. Thus, it is the VEGF-A isoform balance, which is controlled by mRNA splicing, that orchestrates angiogenesis. Here, we highlight the functional differences between the pro-angiogenic and the anti-angiogenic VEGF-A isoform families and the potential to harness the synthetic capacity of cancer cells to produce factors that inhibit, rather than aid, cancer growth.
Figures


References
-
- Mendel DB, et al. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003;9:327–337. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon α in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007;356:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2335–2342. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin. Oncol. 2002;29:10–14. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Henzel WJ. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1989;161:851–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

